A Podocyte-Based Automated Screening Assay Identifies Protective Small Molecules
- PMID: 25858967
- PMCID: PMC4625676
- DOI: 10.1681/ASN.2014090859
A Podocyte-Based Automated Screening Assay Identifies Protective Small Molecules
Abstract
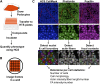
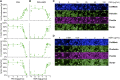
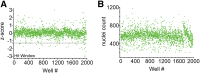
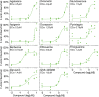
Podocyte injury and loss mark an early step in the pathogenesis of various glomerular diseases, making these cells excellent targets for therapeutics. However, cell-based high-throughput screening assays for the rational development of podocyte-directed therapeutics are currently lacking. Here, we describe a novel high-content screening-based phenotypic assay that analyzes thousands of podocytes per assay condition in 96-well plates to quantitatively measure dose-dependent changes in multiple cellular features. Our assay consistently produced a Z' value >0.44, making it suitable for compound screening. On screening with >2100 pharmacologically active agents, we identified 24 small molecules that protected podocytes against injury in vitro (1% hit rate). Among the identified hits, we confirmed an β1-integrin agonist, pyrintegrin, as a podocyte-protective agent. Treatment with pyrintegrin prevented damage-induced decreases in F-actin stress fibers, focal adhesions, and active β1-integrin levels in cultured cells. In vivo, administration of pyrintegrin protected mice from LPS-induced podocyte foot process effacement and proteinuria. Analysis of the murine glomeruli showed that LPS administration reduced the levels of active β1 integrin in the podocytes, which was prevented by cotreatment with pyrintegrin. In rats, pyrintegrin reduced peak proteinuria caused by puromycin aminonucleoside-induced nephropathy. Our findings identify pyrintegrin as a potential therapeutic candidate and show the use of podocyte-based screening assays for identifying novel therapeutics for proteinuric kidney diseases.
Keywords: adhesion molecule; glomerular disease; glomerular epithelial cells.
Copyright © 2015 by the American Society of Nephrology.
Figures



References
-
- Pavenstädt H, Kriz W, Kretzler M: Cell biology of the glomerular podocyte. Physiol Rev 83: 253–307, 2003 - PubMed
-
- Faul C, Asanuma K, Yanagida-Asanuma E, Kim K, Mundel P: Actin up: Regulation of podocyte structure and function by components of the actin cytoskeleton. Trends Cell Biol 17: 428–437, 2007 - PubMed
-
- Huber TB, Benzing T: The slit diaphragm: A signaling platform to regulate podocyte function. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens 14: 211–216, 2005 - PubMed
-
- Wiggins RC: The spectrum of podocytopathies: A unifying view of glomerular diseases. Kidney Int 71: 1205–1214, 2007 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

