Emotion Knowledge, Loneliness, Negative Social Experiences, and Internalizing Symptoms Among Low-Income Preschoolers
- PMID: 25859097
- PMCID: PMC4386756
- DOI: 10.1111/sode.12083
Emotion Knowledge, Loneliness, Negative Social Experiences, and Internalizing Symptoms Among Low-Income Preschoolers
Abstract
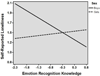
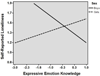
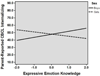
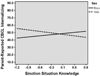
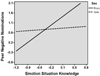
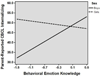
Children with poor emotion knowledge (EK) skills are at risk for externalizing problems; less is known about early internalizing behavior. We examined multiple facets of EK and social-emotional experiences relevant for internalizing difficulties, including loneliness, victimization, and peer rejection, in Head Start preschoolers (N = 134; M = 60 months). Results based on multiple informants suggest that facets of EK are differentially related to negative social-emotional experiences and internalizing behavior and that sex plays a moderating role. Behavioral EK was associated with self-reported loneliness, victimization/rejection, and parent-reported internalizing symptoms. Emotion recognition and expressive emotion knowledge were related to self-reported loneliness, and emotion situation knowledge was related to parent-reported internalizing symptoms and negative peer nominations. Sex moderated many of these associations, suggesting that EK may operate differently for girls versus boys in the preschool social context. Results are discussed with regard to the role of EK for social development and intervention implications.
Figures
References
-
- Achenbach TM, Rescorla LA. Manual for the ASEBA School-Age Forms & Profiles. Burlington, VT: University of Vermont, Research Center for Children, Youth, & Families; 2001.
-
- Arsenio WF, Cooperman S, Lover A. Affective predictors of preschoolers' aggression and peer acceptance: Direct and indirect effects. Developmental Psychology. 2000;36:438–448. - PubMed
-
- Asher SR, Rose AJ, Gabriel SW. Peer rejection in everyday life. In: Leary MR, editor. Interpersonal rejection. New York, NY: Oxford University Press; 2001. pp. 105–142.
-
- Barrett LF, Gross J, Christensen TC, Benvenuto M. Knowing what you're feeling and knowing what to do about it: Mapping the relation between emotion differentiation and emotion regulation. Cognition & Emotion. 2001;15:713–724.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
