A requirement for hedgehog signaling in thyroid hormone-induced postembryonic intestinal remodeling
- PMID: 25859319
- PMCID: PMC4391142
- DOI: 10.1186/s13578-015-0004-3
A requirement for hedgehog signaling in thyroid hormone-induced postembryonic intestinal remodeling
Abstract
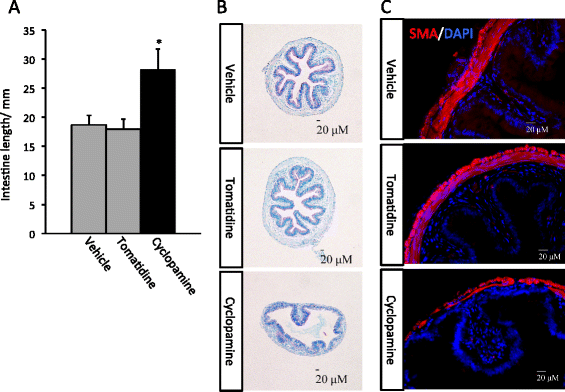
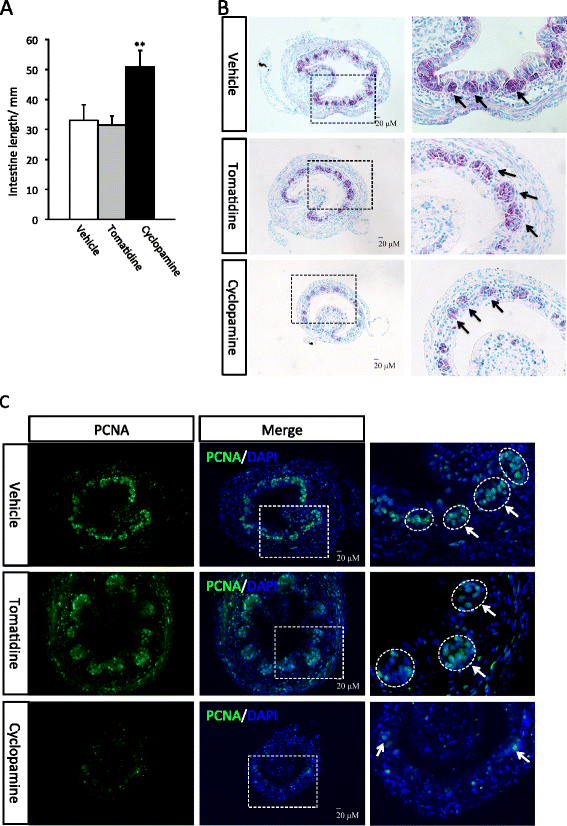
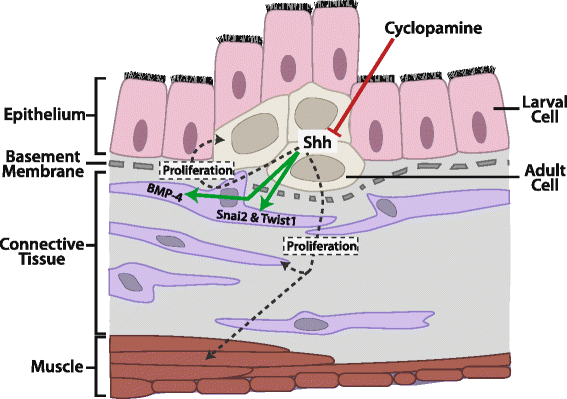
Background: Intestinal remodeling during amphibian metamorphosis has long been studied as a model for the formation of the adult organs in vertebrates, especially the formation of adult organ-specific stem cells. Like all other processes during metamorphosis, this process is controlled by thyroid hormone (T3), which affects cell fate and behavior through transcriptional regulation of target genes by binding to T3 receptors (TRs). Earlier studies have shown that Sonic hedgehog (Shh) is induced by T3 in the developing adult stem cells and that the Shh receptor and other downstream components are present in the connective tissue and at lower levels in the muscles at the climax of intestinal remodeling. However, no in vivo studies have carried out to investigate whether Shh produced in the adult cells can regulate the connective tissue to promote intestinal maturation.
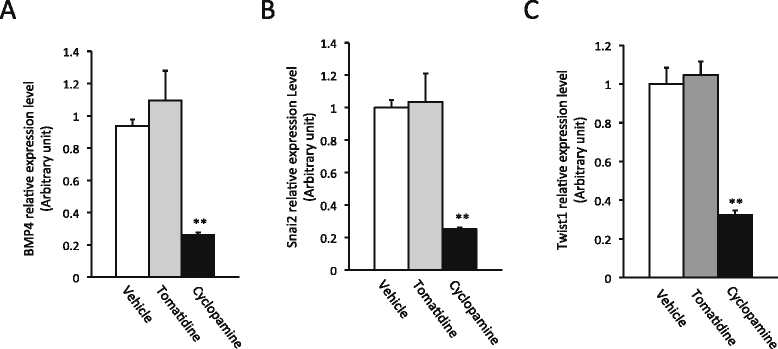
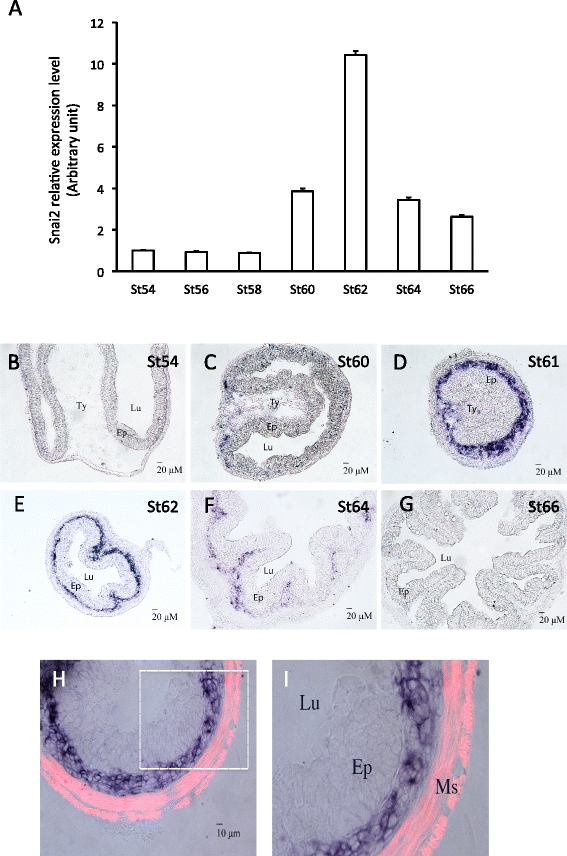
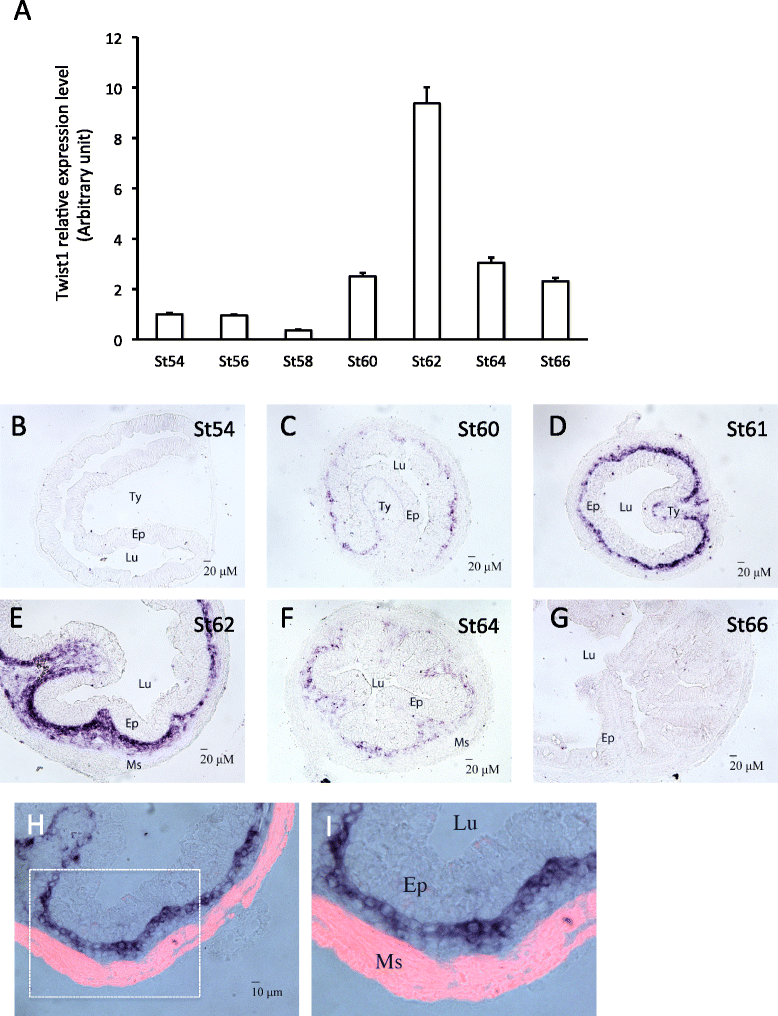
Results: We have addressed this issue by treating tadpoles with Shh inhibitor cyclopamine. We showed that cyclopamine but not the structurally related chemical tomatidine inhibited the expression of Shh response genes BMP4, Snai2, and Twist1. More importantly, we showed that cyclopamine reduced the cell proliferation of both the developing adult stem cells as well as cells in the other intestinal tissues at the climax of metamorphosis, leading to delayed/incomplete remodeling of the intestine at the end of metamorphosis. We further revealed that both Snai2 and Twist1 were strongly upregulated during metamorphosis in the intestine and their expression was restricted to the connective tissue.
Conclusions: Our results suggest that Shh indeed signals the connective tissue whereby it can increase adult stem cell proliferation and promote formation of the adult intestine.
Keywords: Adult stem cells; Amphibian metamorphosis; Postembryonic development; Thyroid hormone receptor; Xenopus laevis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Thyroid hormone-induced expression of sonic hedgehog correlates with adult epithelial development during remodeling of the Xenopus stomach and intestine.Differentiation. 2001 Dec;69(1):27-37. doi: 10.1046/j.1432-0436.2001.690103.x. Differentiation. 2001. PMID: 11776392
-
A Role of Endogenous Histone Acetyltransferase Steroid Hormone Receptor Coactivator 3 in Thyroid Hormone Signaling During Xenopus Intestinal Metamorphosis.Thyroid. 2021 Apr;31(4):692-702. doi: 10.1089/thy.2020.0410. Epub 2020 Nov 20. Thyroid. 2021. PMID: 33076783 Free PMC article.
-
EVI and MDS/EVI are required for adult intestinal stem cell formation during postembryonic vertebrate development.FASEB J. 2018 Jan;32(1):431-439. doi: 10.1096/fj.201700424R. Epub 2017 Sep 19. FASEB J. 2018. PMID: 28928245 Free PMC article.
-
Cell cycle activation in thyroid hormone-induced apoptosis and stem cell development during Xenopus intestinal metamorphosis.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 May 17;14:1184013. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1184013. eCollection 2023. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 37265708 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epigenetic regulation of thyroid hormone-induced adult intestinal stem cell development during anuran metamorphosis.Cell Biosci. 2014 Nov 28;4:73. doi: 10.1186/2045-3701-4-73. eCollection 2014. Cell Biosci. 2014. PMID: 25937894 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Sox transcriptional factors: Functions during intestinal development in vertebrates.Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2017 Mar;63:58-67. doi: 10.1016/j.semcdb.2016.08.022. Epub 2016 Aug 25. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2017. PMID: 27567710 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular regulation of Snai2 in development and disease.J Cell Sci. 2019 Dec 2;132(23):jcs235127. doi: 10.1242/jcs.235127. J Cell Sci. 2019. PMID: 31792043 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Thyroid Hormone Receptor Is Essential for Larval Epithelial Apoptosis and Adult Epithelial Stem Cell Development but Not Adult Intestinal Morphogenesis during Xenopus tropicalis Metamorphosis.Cells. 2021 Mar 3;10(3):536. doi: 10.3390/cells10030536. Cells. 2021. PMID: 33802526 Free PMC article.
-
Sperm associated antigen 7 is activated by T3 during Xenopus tropicalis metamorphosis via a thyroid hormone response element within the first intron.Dev Growth Differ. 2022 Jan;64(1):48-58. doi: 10.1111/dgd.12764. Dev Growth Differ. 2022. PMID: 34862790 Free PMC article.
-
The development of adult intestinal stem cells: Insights from studies on thyroid hormone-dependent anuran metamorphosis.Vitam Horm. 2021;116:269-293. doi: 10.1016/bs.vh.2021.02.010. Epub 2021 Mar 9. Vitam Horm. 2021. PMID: 33752821 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Yen PM. Physiological and molecular basis of thyroid hormone action. Physiol Rev. 2001;81(3):1097–142. - PubMed
-
- Shi Y-B. Amphibian Metamorphosis: From morphology to molecular biology. New York: Wiley; 1999.
-
- Gilbert LI, Tata JR, Atkinson BG. Metamorphosis: Post-embryonic reprogramming of gene expression in amphibian and insect cells. New York: Academic; 1996.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

