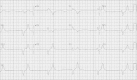
Life-threatening hyperkalemia in a patient with normal renal function
- PMID: 25859350
- PMCID: PMC4389164
- DOI: 10.1093/ckj/sft151
Life-threatening hyperkalemia in a patient with normal renal function
Abstract
With media focus on benefits from reducing sodium intake, there is increased popularity of salt substitutes, typically potassium chloride. While viewed by the public as a healthy alternative to standard table salt, less appreciated is the severe risk with certain comorbidities and medications. We report the case of an elderly female with chronically high salt substitute intake, normal renal function, diabetes, hypertension treated with angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor and beta blockade, who developed life-threatening hyperkalemia after a minimally invasive outpatient procedure. We describe the pathophysiology of the disruption in potassium homeostasis and emphasize the importance of dietary history and educating high-risk patients to avoid salt substitutes.
Keywords: ACE inhibition; arrhythmia; hyperkalemia; salt; salt substitute.
Figures
References
-
- Great Britain. Salt and Health. London: TSO; 2003. Scientific advisory committee on nutrition.
-
- Grande Villoria J, Macias Nunez JF, Miralles JM, et al. Hyporeninemic hypoaldosteronism in diabetic patients with chronic renal failure. Am J Nephrol. 1988;8:127–137. - PubMed
-
- Lundborg P. The effect of adrenergic blockade on potassium concentrations in different conditions. Acta Med Scand Suppl. 1983;672:121–126. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous