The natural compound chebulagic acid inhibits vascular endothelial growth factor A mediated regulation of endothelial cell functions
- PMID: 25859636
- PMCID: PMC4819393
- DOI: 10.1038/srep09642
The natural compound chebulagic acid inhibits vascular endothelial growth factor A mediated regulation of endothelial cell functions
Abstract
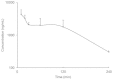
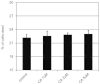
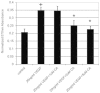
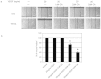
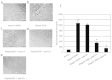
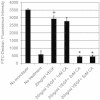
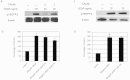
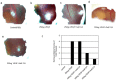
Vascular endothelial growth factor A (VEGFA) plays an important role in tumour angiogenesis and its angiogenic action is mainly mediated through its VEGF receptor 2 (VEGFR-2). Therefore drugs targeting VEGFA/VEGFR-2 are being presently used in the clinics for treatment of several types of solid malignant tumours. We here in report that low dose of chebulagic acid (CA), a hydrolysable tannin found in myrobalan fruits can inhibit VEGFA induced vascular permeability, endothelial cell proliferation, migration, tube formation and thereby, angiogenesis by suppressing VEGFR-2 phosphorylation. CA may thus be an effective and useful natural inhibitor of VEGFA mediated angiogenesis.
Figures
References
-
- Dvorak H. F. Vascular permeability factor/vascular endothelial growth factor: a critical cytokine in tumor angiogenesis and a potential target for diagnosis and therapy. J. Clin. Oncol. 20, 4368–4380 (2002). - PubMed
-
- Ferrara N. Vascular endothelial growth factor. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 29, 789–791 (2009). - PubMed
-
- Sloan B. & Scheinfeld N. S. Pazopanib, a VEGF receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitor for cancer therapy. Curr. Opin. Investig. Drugs. 9, 1324–1335 (2008). - PubMed
-
- Niraula S., Amir E., Vera-Badillo F., Seruga B., Ocana A. & Tannock I. F. Risk of incremental toxicities and associated costs of new anticancer drugs: a meta-analysis. J. Clin. Oncol. 32, 3634–3642 (2014). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

