Health economic evaluation of type 2 diabetes mellitus: a clinical practice focused review
- PMID: 25861233
- PMCID: PMC4374638
- DOI: 10.4137/CMED.S20906
Health economic evaluation of type 2 diabetes mellitus: a clinical practice focused review
Abstract
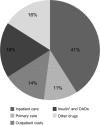
Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2D) is a growing healthcare burden primarily due to long-term complications. Strict glycemic control helps in preventing complications, and early introduction of insulin may be more cost-effective than maintaining patients on multiple oral agents. This is an expert opinion review based on English peer-reviewed articles (2000-2012) to discuss the health economic consequences of T2D treatment intensification. T2D costs are driven by inpatient care for treatment of diabetes complications (40%-60% of total cost), with drug therapy for glycemic control representing 18% of the total cost. Insulin therapy provides the most improved glycemic control and reduction of complications, although hypoglycemia and weight gain may occur. Early treatment intensification with insulin analogs in patients with poor glycemic control appears to be cost-effective and improves clinical outcomes.
Keywords: cost-effectiveness; healthcare economics (operational domain); hyperglycemia; hypoglycemia; insulin; oral antidiabetic agents; type 2 diabetes (clinical domain).
Figures
References
-
- Farag YM, Gaballa MR. Diabesity: an overview of a rising epidemic. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2011;26(1):28–35. - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization . Diabetes Factsheet. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2013.
-
- Currie CJ, Gale EA, Poole CD. Estimation of primary care treatment costs and treatment efficacy for people with Type 1 and Type 2 diabetes in the United Kingdom from 1997 to 2007*. Diabet Med. 2010;27(8):938–948. - PubMed
-
- Massi-Benedetti M. The cost of diabetes Type II in Europe: the CODE-2 Study. Diabetologia. 2002;45(7):S1–S4. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

