Massive pulmonary hemorrhage in enterovirus 71-infected hand, foot, and mouth disease
- PMID: 25861335
- PMCID: PMC4388973
- DOI: 10.3345/kjp.2015.58.3.112
Massive pulmonary hemorrhage in enterovirus 71-infected hand, foot, and mouth disease
Abstract
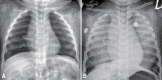
Hand, foot, and mouth disease (HFMD) is an acute, mostly self-limiting infection. Patients usually recover without any sequelae. However, a few cases are life threatening, especially those caused by enterovirus 71 (EV71). A 12-month-old boy was admitted to a primary hospital with high fever and vesicular lesions of the mouth, hands, and feet. After 3 days, he experienced 3 seizure episodes and was referred to our hospital. On admission, he was conscious and his chest radiograph was normal. However, 6 hours later, he suddenly lost consciousness and had developed a massive pulmonary hemorrhage that continued until his death. He experienced several more intermittent seizures, and diffuse infiltration of both lung fields was observed on chest radiography. Intravenous immunoglobulin, dexamethasone, cefotaxime, leukocyte-depleted red blood cells, fresh frozen plasma, inotropics, vitamin K, and endotracheal epinephrine were administered. The patient died 9 hours after intubation, within 3 days from fever onset. EV71 subgenotype C4a was isolated retrospectively from serum and nasopharyngeal swab by real-time reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction. Here, we report a fatal case of EV71-associated HFMD with sudden-onset massive pulmonary hemorrhage and suspected encephalitis.
Keywords: Encephalitis; Enterovirus 71; Hand, foot, and mouth disease; Pulmonary hemorrhage.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures
References
-
- Chen KT, Chang HL, Wang ST, Cheng YT, Yang JY. Epidemiologic features of hand-foot-mouth disease and herpangina caused by enterovirus 71 in Taiwan, 1998-2005. Pediatrics. 2007;120:e244–e252. - PubMed
-
- Zhang YC, Jiang SW, Gu WZ, Hu AR, Lu CT, Liang XY, et al. Clinicopathologic features and molecular analysis of enterovirus 71 infection: report of an autopsy case from the epidemic of hand, foot and mouth disease in China. Pathol Int. 2012;62:565–570. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous