Techniques and applications of in vivo diffusion imaging of articular cartilage
- PMID: 25865215
- PMCID: PMC4439325
- DOI: 10.1002/jmri.24767
Techniques and applications of in vivo diffusion imaging of articular cartilage
Abstract
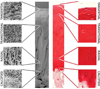
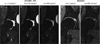
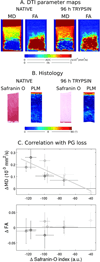
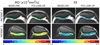
Early in the process of osteoarthritis (OA) the composition (water, proteoglycan [PG], and collagen) and structure of articular cartilage is altered leading to changes in its mechanical properties. A technique that can assess the composition and structure of the cartilage in vivo can provide insight in the mechanical integrity of articular cartilage and become a powerful tool for the early diagnosis of OA. Diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) has been proposed as a biomarker for cartilage composition and structure. DTI is sensitive to the PG content through the mean diffusivity and to the collagen architecture through the fractional anisotropy. However, the acquisition of DTI of articular cartilage in vivo is challenging due to the short T2 of articular cartilage (∼40 ms at 3 Tesla) and the high resolution needed (0.5-0.7 mm in plane) to depict the cartilage anatomy. We describe the pulse sequences used for in vivo DTI of articular cartilage and discus general strategies for protocol optimization. We provide a comprehensive review of measurements of DTI of articular cartilage from ex vivo validation experiments to its recent clinical applications.
Keywords: articular cartilage; diffusion tensor imaging; diffusion-weighted imaging; knee injury; osteoarthritis.
© 2015 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Spatial variations in magnetic resonance-based diffusion of articular cartilage in knee osteoarthritis.Magn Reson Imaging. 2015 Nov;33(9):1051-1058. doi: 10.1016/j.mri.2015.06.004. Epub 2015 Jun 26. Magn Reson Imaging. 2015. PMID: 26119421 Free PMC article.
-
In vivo structural analysis of articular cartilage using diffusion tensor magnetic resonance imaging.Magn Reson Imaging. 2009 Nov;27(9):1242-8. doi: 10.1016/j.mri.2009.05.012. Epub 2009 Jun 23. Magn Reson Imaging. 2009. PMID: 19553054
-
Feasibility of in vivo diffusion tensor imaging of articular cartilage with coverage of all cartilage regions.Eur Radiol. 2014 Jul;24(7):1700-6. doi: 10.1007/s00330-014-3155-4. Epub 2014 May 10. Eur Radiol. 2014. PMID: 24816930
-
MR imaging of articular cartilage physiology.Magn Reson Imaging Clin N Am. 2011 May;19(2):249-82. doi: 10.1016/j.mric.2011.02.010. Magn Reson Imaging Clin N Am. 2011. PMID: 21665090 Free PMC article. Review.
-
New techniques for cartilage imaging: T2 relaxation time and diffusion-weighted MR imaging.Radiol Clin North Am. 2005 Jul;43(4):641-53, vii. doi: 10.1016/j.rcl.2005.02.007. Radiol Clin North Am. 2005. PMID: 15893528 Review.
Cited by
-
Diffusion Tensor Imaging of the Knee to Predict Childhood Growth.Radiology. 2022 Jun;303(3):655-663. doi: 10.1148/radiol.210484. Epub 2022 Mar 22. Radiology. 2022. PMID: 35315716 Free PMC article.
-
Tractography of Porcine Meniscus Microstructure Using High-Resolution Diffusion Magnetic Resonance Imaging.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 May 10;13:876784. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.876784. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35620393 Free PMC article.
-
Diffusion tensor imaging of articular cartilage using a navigated radial imaging spin-echo diffusion (RAISED) sequence.Eur Radiol. 2019 May;29(5):2598-2607. doi: 10.1007/s00330-018-5780-9. Epub 2018 Oct 31. Eur Radiol. 2019. PMID: 30382348 Free PMC article.
-
Detecting early stage osteoarthritis by optical coherence tomography?Biomarkers. 2015;20(8):590-6. doi: 10.3109/1354750X.2015.1130190. Epub 2016 Feb 10. Biomarkers. 2015. PMID: 26862954 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The QIBA Profile for MRI-based Compositional Imaging of Knee Cartilage.Radiology. 2021 Nov;301(2):423-432. doi: 10.1148/radiol.2021204587. Epub 2021 Sep 7. Radiology. 2021. PMID: 34491127 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Mox VC, Gu WY, Chen FH. Structure and function of articular cartilage. In: Mow VC, Huiskes R, editors. Basic Orthopedics biomechanics and mechano-biology. 3rd ed. Philadelphia, PA, US: Lippincott Willians & Wilkins; 2005. pp. 123–180.
-
- Maroudas AI. Balance between swelling pressure and collagen tension in normal and degenerate cartilage. Nature. 1976;260(5554):808–809. - PubMed
-
- Maroudas A, Baylissb MT, Uchitel-Kaushanskya N, Schneidermana R, Gilav E. Aggrecan turnover in human articular cartilage: Use of aspartic acid racemization as a marker of molecular age. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1998;350:61–71. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

