Immunology of IgG4-related disease
- PMID: 25865251
- PMCID: PMC4516435
- DOI: 10.1111/cei.12641
Immunology of IgG4-related disease
Abstract
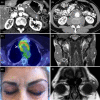
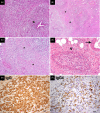
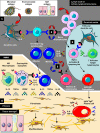
Immunoglobulin G4-related disease (IgG4-RD) is a fibroinflammatory condition that derives its name from the characteristic finding of abundant IgG4(+) plasma cells in affected tissues, as well as the presence of elevated serum IgG4 concentrations in many patients. In contrast to fibrotic disorders, such as systemic sclerosis or idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis in which the tissues fibrosis has remained largely intractable to treatment, many IgG4-RD patients appear to have a condition in which the collagen deposition is reversible. The mechanisms underlying this peculiar feature remain unknown, but the remarkable efficacy of B cell depletion in these patients supports an important pathogenic role of B cell/T cell collaboration. In particular, aberrant T helper type 2 (Th2)/regulatory T cells sustained by putative autoreactive B cells have been proposed to drive collagen deposition through the production of profibrotic cytokines, but definitive demonstrations of this hypothesis are lacking. Indeed, a number of unsolved questions need to be addressed in order to fully understand the pathogenesis of IgG4-RD. These include the identification of an antigenic trigger(s), the implications (if any) of IgG4 antibodies for pathophysiology and the precise immunological mechanisms leading to fibrosis. Recent investigations have also raised the possibility that innate immunity might precede adaptive immunity, thus further complicating the pathological scenario. Here, we aim to review the most recent insights on the immunology of IgG4-RD, focusing on the relative contribution of innate and adaptive immune responses to the full pathological phenotype of this fibrotic condition. Clinical, histological and therapeutic features are also addressed.
Keywords: IgG4; IgG4-related disease; immunology; pathogenesis; review.
© 2015 British Society for Immunology.
Figures


References
-
- Hamano H, Kawa S, Horiuchi A. High serum IgG4 concentrations in patients with sclerosing pancreatitis. N Engl J Med. 2011;344:732–8. - PubMed
-
- Stone JH, Zen Y, Deshpande V, et al. IgG4-related disease. N Engl J Med. 2012;366:539–51. - PubMed
-
- Deshpande V, Zen Y, Chan JK. Consensus statement on the pathology of IgG4-related disease. Mod Pathol. 2012;25:1181–92. - PubMed
-
- Umehara H, Okazaki K, Masaki Y, et al. Comprehensive diagnostic criteria for IgG4-related disease (IgG4-RD), 2011. Mod Rheumatol. 2012;22:21–30. - PubMed
-
- Kanno A, Nishimori I, Masamune Aetal, et al. Nationwide epidemiological survey of autoimmune pancreatitis in Japan. Pancreas. 2012;41:835–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

