Enhanced extraction of bovine serum albumin with aqueous biphasic systems of phosphonium- and ammonium-based ionic liquids
- PMID: 25865275
- PMCID: PMC5034895
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jbiotec.2015.03.028
Enhanced extraction of bovine serum albumin with aqueous biphasic systems of phosphonium- and ammonium-based ionic liquids
Abstract
Novel aqueous biphasic systems (ABS) composed of phosphonium- or ammonium-based ionic liquids (ILs), combined with a buffered aqueous solution of potassium citrate/citric acid (pH=7.0), were investigated for the extraction of proteins. For that purpose, the phase diagrams, tie-lines and tie-line lengths were determined at 25 °C, and the performance of these ABS for the extraction of bovine serum albumin (BSA) was then evaluated. The obtained results reveal that, with the exception of the more hydrophobic ILs, most of the systems investigated allow the complete extraction of BSA for the IL-rich phase in a single-step. These remarkable extraction efficiencies are far superior to those afforded by more conventional extraction systems previously reported. The composition of the biphasic systems, i.e., the amount of phase-forming components, was also investigated aiming at reducing the overall costs of the process without losing efficiency on the protein extraction. It is shown that the extraction efficiencies of BSA are maintained at 100% up to high protein concentrations (at least up to 10 g L(-1)). The recovery of the BSA from the IL-rich phase by dialysis is also shown in addition to the demonstration of the IL recyclability and reusability, at least for 3 times. In the sequential three-step extractions (BSA recovery/IL reusability), the extraction efficiencies of BSA for the IL-rich phase were maintained at 100%. For the improved ABS, the preservation of the protein native conformation was confirmed by Size Exclusion High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (used also as the quantification method) and by Fourier Transform Infra-Red spectroscopy. According to the results herein reported, ABS composed of phosphonium- or ammonium-based ILs and a biodegradable organic salt represent an alternative and remarkable platform for the extraction of BSA and may be extended to other proteins of interest.
Keywords: Aqueous biphasic system; Bovine serum albumin (BSA); Extraction; Ionic liquid; Native conformation; Protein.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures
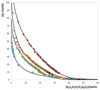
 ); [P4441][MeSO4] (
); [P4441][MeSO4] ( ); [P4444]Cl (
); [P4444]Cl ( ); [Pi(444)1][Tos] (
); [Pi(444)1][Tos] ( ); and adjusted binodal data through Eq. (1) (–).
); and adjusted binodal data through Eq. (1) (–).
 ); [N4444]Cl (
); [N4444]Cl ( ); and adjusted binodal data through Eq. (1) (–).
); and adjusted binodal data through Eq. (1) (–).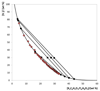
 ); TL data (■); and adjusted binodal data through Eq. (1) (–).
); TL data (■); and adjusted binodal data through Eq. (1) (–).

Similar articles
-
Enhanced extraction of proteins using cholinium-based ionic liquids as phase-forming components of aqueous biphasic systems.Biotechnol J. 2015 Sep;10(9):1457-66. doi: 10.1002/biot.201500003. Epub 2015 Apr 30. Biotechnol J. 2015. PMID: 25864445
-
Extraction of biomolecules using phosphonium-based ionic liquids + K(3)PO(4) aqueous biphasic systems.Int J Mol Sci. 2010 Apr 15;11(4):1777-91. doi: 10.3390/ijms11041777. Int J Mol Sci. 2010. PMID: 20480041 Free PMC article.
-
Aqueous biphasic systems composed of ionic liquids and sodium carbonate as enhanced routes for the extraction of tetracycline.Biotechnol Prog. 2013 May-Jun;29(3):645-54. doi: 10.1002/btpr.1708. Epub 2013 Mar 29. Biotechnol Prog. 2013. PMID: 23420737
-
Chiral Ionic Liquids: Structural Diversity, Properties and Applications in Selected Separation Techniques.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Jun 15;21(12):4253. doi: 10.3390/ijms21124253. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32549300 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Applications of ionic liquids in biphasic separation: Aqueous biphasic systems and liquid-liquid equilibria.J Chromatogr A. 2018 Jul 20;1559:44-61. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2017.10.019. Epub 2017 Oct 10. J Chromatogr A. 2018. PMID: 29054438 Review.
Cited by
-
Advances Brought by Hydrophilic Ionic Liquids in Fields Involving Pharmaceuticals.Materials (Basel). 2021 Oct 20;14(21):6231. doi: 10.3390/ma14216231. Materials (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34771756 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Separation of immunoglobulin G using aqueous biphasic systems composed of cholinium-based ionic liquids and poly(propylene glycol).J Chem Technol Biotechnol. 2018 Jul;93(7):1931-1939. doi: 10.1002/jctb.5594. Epub 2018 Jan 31. J Chem Technol Biotechnol. 2018. PMID: 30270961 Free PMC article.
-
New liquid supports in the development of integrated platforms for the reuse of oxidative enzymes and polydopamine production.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022 Nov 28;10:1037322. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2022.1037322. eCollection 2022. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022. PMID: 36518198 Free PMC article.
-
Do Ionic Liquids Exhibit the Required Characteristics to Dissolve, Extract, Stabilize, and Purify Proteins? Past-Present-Future Assessment.Chem Rev. 2024 Mar 27;124(6):3037-3084. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.3c00551. Epub 2024 Mar 4. Chem Rev. 2024. PMID: 38437627 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Glycine-betaine ionic liquid analogues as novel phase-forming components of aqueous biphasic systems.Biotechnol Prog. 2018 Sep;34(5):1205-1212. doi: 10.1002/btpr.2685. Epub 2018 Aug 10. Biotechnol Prog. 2018. PMID: 30006961 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Albertsson PA. Partition of cell particles and macromolecules: separation and purification of biomolecules, cell organelles, membranes, and cells in aqueous polymer two-phase systems and their use in biochemical analysis and biotechnology. Wiley; New York: 1986.
-
- Albertsson PA. Partition of proteins in liquid polymer-polymer two-phase systems. Nature. 1958;182:709–711. - PubMed
-
- Alvarez-Guerra E, Irabien A. Extraction of lactoferrin with hydrophobic ionic liquids. Sep Purif Technol. 2012;98:432–440.
-
- Arakawa T, Kita Y, Timasheff SN. Protein precipitation and denaturation by dimethyl sulfoxide. Biophys Chem. 2007;131:62–70. - PubMed
-
- Asenjo JA, Andrews BA. Aqueous two-phase systems for protein separation: a perspective. J Chromatogr A. 2011;1218:8826–35. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

