The role of the kynurenine pathway in suicidality in adolescent major depressive disorder
- PMID: 25865484
- PMCID: PMC4430385
- DOI: 10.1016/j.psychres.2015.03.031
The role of the kynurenine pathway in suicidality in adolescent major depressive disorder
Abstract
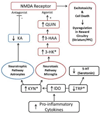
The neuroimmunological kynurenine pathway (KP) has been implicated in major depressive disorder (MDD) in adults and adolescents, most recently in suicidality in adults. The KP is initiated by the enzyme indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO), which degrades tryptophan (TRP) into kynurenine (KYN) en route to neurotoxins. Here, we examined the KP in 20 suicidal depressed adolescents-composed of past attempters and those who expressed active suicidal intent-30 non-suicidal depressed youth, and 22 healthy controls (HC). Plasma levels of TRP, KYN, 3-hydroxyanthranilic acid (3-HAA), and KYN/TRP (index of IDO) were assessed. Suicidal adolescents showed decreased TRP and elevated KYN/TRP compared to both non-suicidal depressed adolescents and HC. Findings became more significantly pronounced when excluding medicated participants, wherein there was also a significant positive correlation between KYN/TRP and suicidality. Finally, although depressed adolescents with a history of suicide attempt differed from acutely suicidal adolescents with respect to disease severity, anhedonia, and suicidality, the groups did not differ in KP measures. Our findings suggest a possible specific role of the KP in suicidality in depressed adolescents, while illustrating the clinical phenomenon that depressed adolescents with a history of suicide attempt are similar to acutely suicidal youth and are at increased risk for completion of suicide.
Keywords: 3-dioxygenase; 3-hydroxyanthranilic acid; Adolescence; Depression; Indoleamine 2; Suicide; Tryptophan.
Published by Elsevier Ireland Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest to report for any of the authors on this manuscript.
Figures


References
-
- Almeida-Montes LG, Valles-Sanchez V, Moreno-Aguilar J, Chavez-Balderas RA, Garcia-Marin JA, Cortés Sotres JF, Hheinze-Martin G. Relation of serum cholesterol, lipid, serotonin and tryptophan levels to severity of depression and to suicide attempts. Journal of Psychiatry & Neuroscience. 2000;25:371–377. - PMC - PubMed
-
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. 4th ed. Washington, DC: 2000. text rev. Author.
-
- Bay-Richter C, Linderholm KR, Lim CK, Samuelsson M, Träskman-Bendz L, Guillemin GJ, Erhardt S, Brundin L. A role for inflammatory metabolites as modulators of the glutamate N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor in depression and suicidality. Brain, Behavior, and Immunity. 2015;43:110–117. - PubMed
-
- Brent DA, Perper JA, Moritz G, Allman C, Friend A, Roth C, Schweers J, Balach L, Baugher M. Psychiatric risk factors of adolescent suicide: a case control study. Journal of the American Academy of Child & Adolescent Psychiatry. 1993;32:521–529. - PubMed
-
- Brown GK, Beck AT, Steer RA, Grisham JR. Risk factors for suicide in psychiatric outpatients: a 20-year prospective study. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology. 2000;68:371–377. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

