Resveratrol prevents protein nitration and release of endonucleases from mitochondria during acetaminophen hepatotoxicity
- PMID: 25865938
- PMCID: PMC4450137
- DOI: 10.1016/j.fct.2015.04.014
Resveratrol prevents protein nitration and release of endonucleases from mitochondria during acetaminophen hepatotoxicity
Abstract
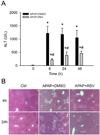
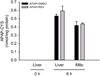
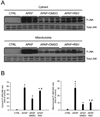
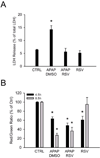
Overdose of acetaminophen (APAP) is a common cause of acute liver injury and liver failure. The mechanism involves formation of a reactive metabolite, protein binding, oxidative stress and activation of c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK), mitochondrial dysfunction, and nuclear DNA fragmentation caused by endonucleases released from damaged mitochondria. Previous work has shown that the natural product resveratrol (RSV) can protect against APAP hepatotoxicity in mice through prevention of lipid peroxidation and anti-inflammatory effects. However, these earlier studies did not take into consideration several fundamental aspects of the pathophysiology. To address this, we treated C57Bl/6 mice with 300 mg/kg APAP followed by 50 mg/kg RSV 1.5 h later. Our results confirmed that RSV reduced liver injury after APAP overdose in mice. Importantly, RSV did not inhibit reactive metabolite formation and protein bindings, nor did it reduce activation of JNK. However, RSV decreased protein nitration after APAP treatment, possibly through direct scavenging of peroxynitrite. Interestingly, RSV also inhibited release of apoptosis-inducing factor and endonuclease G from mitochondria independent of Bax pore formation and prevented the downstream nuclear DNA fragmentation. Our data show that RSV protects against APAP hepatotoxicity both through antioxidant effects and by preventing mitochondrial release of endonucleases and nuclear DNA damage.
Keywords: Acetaminophen; DNA fragmentation; Drug hepatotoxicity; Mitochondrial dysfunction; Oxidant stress; Resveratrol.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Ahn J, Cho I, Kim S, Kwon D, Ha T. Dietary resveratrol alters lipid metabolism-related gene expression of mice on an atherogenic diet. J. Hepatol. 2008;49:1019–1028. - PubMed
-
- Antoniades CG, Quaglia A, Taams LS, Mitry RR, Hussain M, Abeles R, Possamai LA, Bruce M, McPhail M, Starling C, Wagner B, Barnardo A, Pomplun S, Auzinger G, Bernal W, Heaton N, Vergani D, Thursz MR, Wendon J. Source and characterization of hepatic macrophages in acetaminophen-induced acute liver failure in humans. Hepatology. 2012;56:735–746. - PubMed
-
- Bajt ML, Cover C, Lemasters JJ, Jaeschke H. Nuclear translocation of endonuclease G and apoptosis-inducing factor during acetaminophen-induced liver injury. Toxicol. Sci. 2006;94:217–225. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

