Endothelium and NOTCH specify and amplify aorta-gonad-mesonephros-derived hematopoietic stem cells
- PMID: 25866967
- PMCID: PMC4463208
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI80137
Endothelium and NOTCH specify and amplify aorta-gonad-mesonephros-derived hematopoietic stem cells
Abstract
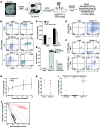
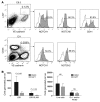
Hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) first emerge during embryonic development within vessels such as the dorsal aorta of the aorta-gonad-mesonephros (AGM) region, suggesting that signals from the vascular microenvironment are critical for HSC development. Here, we demonstrated that AGM-derived endothelial cells (ECs) engineered to constitutively express AKT (AGM AKT-ECs) can provide an in vitro niche that recapitulates embryonic HSC specification and amplification. Specifically, nonengrafting embryonic precursors, including the VE-cadherin-expressing population that lacks hematopoietic surface markers, cocultured with AGM AKT-ECs specified into long-term, adult-engrafting HSCs, establishing that a vascular niche is sufficient to induce the endothelial-to-HSC transition in vitro. Subsequent to hematopoietic induction, coculture with AGM AKT-ECs also substantially increased the numbers of HSCs derived from VE-cadherin⁺CD45⁺ AGM hematopoietic cells, consistent with a role in supporting further HSC maturation and self-renewal. We also identified conditions that included NOTCH activation with an immobilized NOTCH ligand that were sufficient to amplify AGM-derived HSCs following their specification in the absence of AGM AKT-ECs. Together, these studies begin to define the critical niche components and resident signals required for HSC induction and self-renewal ex vivo, and thus provide insight for development of defined in vitro systems targeted toward HSC generation for therapeutic applications.
Figures





References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

