Natural genetic variation in Arabidopsis thaliana defense metabolism genes modulates field fitness
- PMID: 25867014
- PMCID: PMC4396512
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.05604
Natural genetic variation in Arabidopsis thaliana defense metabolism genes modulates field fitness
Abstract
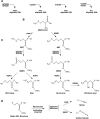
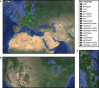
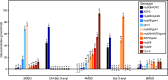
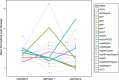
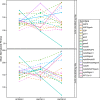
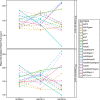
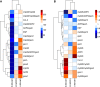
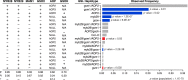
Natural populations persist in complex environments, where biotic stressors, such as pathogen and insect communities, fluctuate temporally and spatially. These shifting biotic pressures generate heterogeneous selective forces that can maintain standing natural variation within a species. To directly test if genes containing causal variation for the Arabidopsis thaliana defensive compounds, glucosinolates (GSL) control field fitness and are therefore subject to natural selection, we conducted a multi-year field trial using lines that vary in only specific causal genes. Interestingly, we found that variation in these naturally polymorphic GSL genes affected fitness in each of our environments but the pattern fluctuated such that highly fit genotypes in one trial displayed lower fitness in another and that no GSL genotype or genotypes consistently out-performed the others. This was true both across locations and within the same location across years. These results indicate that environmental heterogeneity may contribute to the maintenance of GSL variation observed within Arabidopsis thaliana.
Keywords: arabidopsis; ecology; evolutionary biology; fitness; genomics; glucosinolates; herbivory; natural variation; plant defense.
Conflict of interest statement
DJK, Reviewing editor,
The other authors declare that no competing interests exist.
Figures

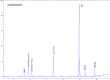
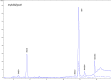
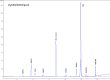
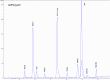


References
-
- Aires A, Carvalho R, Da Conceição Barbosa M, Rosa E. Suppressing potato cyst nematode, globodera rostochiensis, with extracts of brassicacea plants. American Journal of Potato Research. 2009;86:327–333. doi: 10.1007/s12230-009-9086-y. - DOI
-
- Alonso JM, Stepanova AN, Leisse TJ, Kim CJ, Chen H, Shinn P, Stevenson DK, Zimmerman J, Barajas P, Cheuk R, Gadrinab C, Heller C, Jeske A, Koesema E, Meyers CC, Parker H, Prednis L, Ansari Y, Choy N, Deen H, Geralt M, Hazari N, Hom E, Karnes M, Mulholland C, Ndubaku R, Schmidt I, Guzman P, Aguilar-Henonin L, Schmid M, Weigel D, Carter DE, Marchand T, Risseeuw E, Brogden D, Zeko A, Crosby WL, Berry CC, Ecker JR. Genome-wide insertional mutagenesis of Arabidopsis thaliana. Science. 2003;301:653–657. doi: 10.1126/science.1086391. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

