MIC-1/GDF15 in Barrett's oesophagus and oesophageal adenocarcinoma
- PMID: 25867265
- PMCID: PMC4402450
- DOI: 10.1038/bjc.2015.100
MIC-1/GDF15 in Barrett's oesophagus and oesophageal adenocarcinoma
Abstract
Background: Biomarkers are needed to improve current diagnosis and surveillance strategies for patients with Barrett's oesophagus (BO) and oesophageal adenocarcinoma (OAC). Macrophage inhibitory cytokine 1/growth differentiation factor 15 (MIC-1/GDF15) tissue and plasma levels have been shown to predict disease progression in other cancer types and was therefore evaluated in BO/OAC.
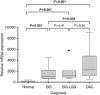
Methods: One hundred thirty-eight patients were studied: 45 normal oesophagus (NE), 37 BO, 16 BO with low-grade dysplasia (LGD) and 40 OAC.
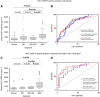
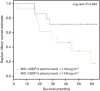
Results: Median tissue expression of MIC-1/GDF15 mRNA was ⩾25-fold higher in BO and LGD compared to NE (P<0.001); two-fold higher in OAC vs BO (P=0.039); and 47-fold higher in OAC vs NE (P<0.001). Relative MIC-1/GDF15 tissue expression >720 discriminated between the presence of either OAC or LGD vs NE with 94% sensitivity and 71% specificity (ROC AUC 0.86, 95% CI 0.73-0.96; P<0.001). Macrophage inhibitory cytokine 1/growth differentiation factor 15 plasma values were also elevated in patients with OAC vs NE (P<0.001) or BO (P=0.015).High MIC-1/GDF15 plasma levels (⩾1140 pg ml(-1)) were an independent predictor of poor survival for patients with OAC (HR 3.87, 95% CI 1.01-14.75; P=0.047).
Conclusions: Plasma and tissue levels of MIC-1/GDF15 are significantly elevated in patients with BO, LGD and OAC. Plasma MIC-1/GDF15 may have value in diagnosis and monitoring of Barrett's disease.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Aberrant p53 protein expression is associated with an increased risk of neoplastic progression in patients with Barrett's oesophagus.Gut. 2013 Dec;62(12):1676-83. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2012-303594. Epub 2012 Dec 20. Gut. 2013. PMID: 23256952
-
Impact of surveillance for Barrett's oesophagus on tumour stage and survival of patients with neoplastic progression.Gut. 2016 Apr;65(4):548-54. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2014-308802. Epub 2015 Apr 22. Gut. 2016. PMID: 25903690
-
Barrett's oesophagus patients with low-grade dysplasia can be accurately risk-stratified after histological review by an expert pathology panel.Gut. 2015 May;64(5):700-6. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2014-307278. Epub 2014 Jul 17. Gut. 2015. PMID: 25034523
-
Systematic review with meta-analysis: the effects of family history on the risk of Barrett's oesophagus and oesophageal adenocarcinoma.Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2021 Oct;54(7):868-879. doi: 10.1111/apt.16558. Epub 2021 Aug 12. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2021. PMID: 34383966 Free PMC article.
-
[Barrett's oesophagus: endoscopic diagnosis and follow-up].Ann Chir. 2006 Jan;131(1):3-6. doi: 10.1016/j.anchir.2005.11.003. Epub 2005 Dec 1. Ann Chir. 2006. PMID: 16376849 Review. French.
Cited by
-
A systematic review and meta-analysis of prognostic biomarkers in resectable esophageal adenocarcinomas.Sci Rep. 2018 Sep 5;8(1):13281. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-31548-6. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 30185893 Free PMC article.
-
Growth differentiation factor 15 contributes to marrow adipocyte remodeling in response to the growth of leukemic cells.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2018 Mar 22;37(1):66. doi: 10.1186/s13046-018-0738-y. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2018. PMID: 29566722 Free PMC article.
-
Integrative analysis of genomic, epigenomic and transcriptomic data identified molecular subtypes of esophageal carcinoma.Aging (Albany NY). 2021 Feb 26;13(5):6999-7019. doi: 10.18632/aging.202556. Epub 2021 Feb 26. Aging (Albany NY). 2021. PMID: 33638948 Free PMC article.
-
GDF15 contributes to radioresistance and cancer stemness of head and neck cancer by regulating cellular reactive oxygen species via a SMAD-associated signaling pathway.Oncotarget. 2017 Jan 3;8(1):1508-1528. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.13649. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 27903972 Free PMC article.
-
Gastroesophageal reflux GWAS identifies risk loci that also associate with subsequent severe esophageal diseases.Nat Commun. 2019 Sep 16;10(1):4219. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-11968-2. Nat Commun. 2019. PMID: 31527586 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bauskin AR, Brown DA, Junankar S, Rasiah KK, Eggleton S, Hunter M, Liu T, Smith D, Kuffner T, Pankhurst GJ, Johnen H, Russell PJ, Barret W, Stricker PD, Grygiel JJ, Kench JG, Henshall SM, Sutherland RL, Breit SN. The propeptide mediates formation of stromal stores of PROMIC-1: role in determining prostate cancer outcome. Cancer Res. 2005;65:2330–2336. - PubMed
-
- Bauskin AR, Brown DA, Kuffner T, Johnen H, Luo XW, Hunter M, Breit SN. Role of macrophage inhibitory cytokine-1 in tumorigenesis and diagnosis of cancer. Cancer Res. 2006;66:4983–4986. - PubMed
-
- Bhat SK, McManus DT, Coleman HG, Johnston BT, Cardwell CR, McMenamin U, Bannon F, Hicks B, Kennedy G, Gavin AT, Murray LJ. Oesophageal adenocarcinoma and prior diagnosis of Barrett's oesophagus: a population-based study. Gut. 2014;64:20–25. - PubMed
-
- Bootcov MR, Bauskin AR, Valenzuela SM, Moore AG, Bansal M, He XY, Zhang HP, Donnellan M, Mahler S, Pryor K, Walsh BJ, Nicholson RC, Fairlie WD, Por SB, Robbins JM, Breit SN. MIC-1, a novel macrophage inhibitory cytokine, is a divergent member of the TGF-beta superfamily. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1997;94:11514–11519. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Botelho NK, Schneiders FI, Lord SJ, Freeman AK, Tyagi S, Nancarrow DJ, Hayward NK, Whiteman DC, Lord RV. Gene expression alterations in formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded Barrett esophagus and esophageal adenocarcinoma tissues. Cancer Biol Ther. 2010;10:172–179. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Supplementary concepts
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

