Bilateral optic neuropathy following bite from brown recluse spider (Loxosceles reclusa)
- PMID: 25869060
- PMCID: PMC4605862
- DOI: 10.3109/15569527.2015.1027906
Bilateral optic neuropathy following bite from brown recluse spider (Loxosceles reclusa)
Abstract
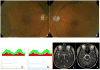
A 63-year-old female with history of a resected frontal lobe meningioma presented with bilaterally decreased vision after a bite from a brown recluse spider. The exam was significant for a left relative afferent pupillary defect, bilateral optic nerve pallor, decreased foveal sensitivity in the left eye and new bilateral visual field defects, despite stability of her meningioma. The findings remained stable at 1-year follow-up. To our knowledge, this is the first reported case of optic neuropathy secondary to a brown recluse spider bite. Visual field tests performed prior to the bite allowed us to compare and localize changes related to the bite.
Keywords: Brown recluse spider; Loxosceles reclusa; envenomation; optic neuropathy; spider bite; toxic.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: None
Figures

Similar articles
-
Coagulation abnormalities following brown recluse spider (Loxosceles reclusa) envenomation: A description of 2 cases and review of the literature.Am J Clin Pathol. 2025 Jun 3;163(6):822-836. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/aqaf001. Am J Clin Pathol. 2025. PMID: 39883062 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Surgical treatment of a brown recluse spider bite: a case study and literature review.J Foot Ankle Surg. 2014 May-Jun;53(3):320-3. doi: 10.1053/j.jfas.2014.01.009. Epub 2014 Mar 22. J Foot Ankle Surg. 2014. PMID: 24666977 Review.
-
A brown recluse spider bite wound: a case report and literature review.J Wound Care. 2024 Jul 1;33(Sup7):S24-S29. doi: 10.12968/jowc.2023.0104. J Wound Care. 2024. PMID: 38973639 Review.
-
Rare case of dermonecrosis caused by a recluse spider bite in Europe.BMJ Case Rep. 2016 Jul 20;2016:bcr2016215832. doi: 10.1136/bcr-2016-215832. BMJ Case Rep. 2016. PMID: 27440851 Free PMC article.
-
Hold the Chemo! Leukostasis, a Presentation of Brown Recluse Spider Bite: A Case Report.J Investig Med High Impact Case Rep. 2021 Jan-Dec;9:23247096211039949. doi: 10.1177/23247096211039949. J Investig Med High Impact Case Rep. 2021. PMID: 34404267 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Acanthocytosis and brain damage in area postrema and choroid plexus: Description of novel signs of Loxosceles apachea envenomation in rats.PLoS One. 2019 Feb 7;14(2):e0211689. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0211689. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 30730934 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical aspects, diagnosis and management of Loxosceles spider envenomation: literature and case review.Arch Toxicol. 2020 May;94(5):1461-1477. doi: 10.1007/s00204-020-02719-0. Epub 2020 Mar 30. Arch Toxicol. 2020. PMID: 32232511 Review.
-
Systemic Loxoscelism, Less Frequent but More Deadly: The Involvement of Phospholipases D in the Pathophysiology of Envenomation.Toxins (Basel). 2022 Dec 27;15(1):17. doi: 10.3390/toxins15010017. Toxins (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36668837 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Goldstein NRCWH. Neuritis occuring after insect stings. JAMA. 1960;173:1727–1730.
-
- Song HS, Wray SH. Bee sting optic neuritis. A case report with visual evoked potentials. J Clin Neuroophthalmol. 1991;11:45–49. - PubMed
-
- Singh I, Chaudhary U. Bilateral optic neuritis following multiple wasp stings. J Indian Med Assoc. 1986;84:251–252. - PubMed
-
- Lesser RL. Ocular manifestations of Lyme disease. Am J Med. 1995;98:60S–62S. - PubMed
-
- Aragao RE, Barreira IM, Lima LN, Rabelo LP, Pereira FB. Bilateral optic neuritis after dengue viral infection: case report. Arq Bras Oftalmol. 2010;73:175–178. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
