Myc-dependent purine biosynthesis affects nucleolar stress and therapy response in prostate cancer
- PMID: 25869206
- PMCID: PMC4494960
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.3494
Myc-dependent purine biosynthesis affects nucleolar stress and therapy response in prostate cancer
Abstract
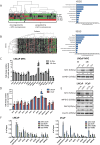
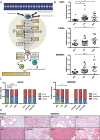
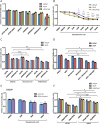
The androgen receptor is a key transcription factor contributing to the development of all stages of prostate cancer (PCa). In addition, other transcription factors have been associated with poor prognosis in PCa, amongst which c-Myc (MYC) is a well-established oncogene in many other cancers. We have previously reported that the AR promotes glycolysis and anabolic metabolism; many of these metabolic pathways are also MYC-regulated in other cancers. In this study, we report that in PCa cells de novo purine biosynthesis and the subsequent conversion to XMP is tightly regulated by MYC and independent of AR activity. We characterized two enzymes, PAICS and IMPDH2, within the pathway as PCa biomarkers in tissue samples and report increased efficacy of established anti-androgens in combination with a clinically approved IMPDH inhibitor, mycophenolic acid (MPA). Treatment with MPA led to a significant reduction in cellular guanosine triphosphate (GTP) levels accompanied by nucleolar stress and p53 stabilization. In conclusion, targeting purine biosynthesis provides an opportunity to perturb PCa metabolism and enhance tumour suppressive stress responses.
Keywords: cancer; metabolism; nucleotide; prostate; transcription.
Figures

References
-
- Feldman BJ, Feldman D. The development of androgen-independent prostate cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2001;1:34–45. - PubMed
-
- van der Kwast TH, Schalken J, Ruizeveld de Winter JA, van Vroonhoven CC, Mulder E, Boersma W, Trapman J. Androgen receptors in endocrine-therapy-resistant human prostate cancer. Int J Cancer. 1991;48:189–193. - PubMed
-
- Sadi MV, Walsh PC, Barrack ER. Immunohistochemical study of androgen receptors in metastatic prostate cancer. Comparison of receptor content and response to hormonal therapy. Cancer. 1991;67:3057–3064. - PubMed
-
- Koivisto P, Kononen J, Palmberg C, Tammela T, Hyytinen E, Isola J, Trapman J, Cleutjens K, Noordzij A, Visakorpi T, Kallioniemi OP. Androgen receptor gene amplification: a possible molecular mechanism for androgen deprivation therapy failure in prostate cancer. Cancer Res. 1997;57:314–319. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

