JAK2 inhibitor TG101348 overcomes erlotinib-resistance in non-small cell lung carcinoma cells with mutated EGF receptor
- PMID: 25869210
- PMCID: PMC4546470
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.3685
JAK2 inhibitor TG101348 overcomes erlotinib-resistance in non-small cell lung carcinoma cells with mutated EGF receptor
Abstract
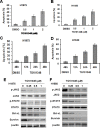
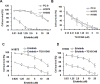
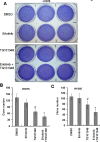
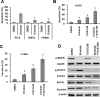
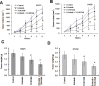
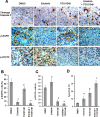
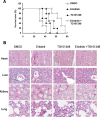
Non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) patients with epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutations are responsive to EGFR-tyrosine kinase inhibitor (EGFR-TKI). However, NSCLC patients with secondary somatic EGFR mutations are resistant to EGFR-TKI treatment. In this study, we investigated the effect of TG101348 (a JAK2 inhibitor) on the tumor growth of erlotinib-resistant NSCLC cells. Cell proliferation, apoptosis, gene expression and tumor growth were evaluated by diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT) assay, flow cytometry, terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase biotin-dUTP nick end labeling (TUNEL) staining, Western Blot and a xenograft mouse model, respectively. Results showed that erlotinib had a stronger impact on the induction of apoptosis in erlotinib-sensitive PC-9 cells but had a weaker effect on erlotinib-resistant H1975 and H1650 cells than TG101348. TG101348 significantly enhanced the cytotoxicity of erlotinib to erlotinib-resistant NSCLC cells, stimulated erlotinib-induced apoptosis and downregulated the expressions of EGFR, p-EGFR, p-STAT3, Bcl-xL and survivin in erlotinib-resistant NSCLC cells. Moreover, the combined treatment of TG101348 and erlotinib induced apoptosis, inhibited the activation of p-EGFR and p-STAT3, and inhibited tumor growth of erlotinib-resistant NSCLC cells in vivo. Our results indicate that TG101348 is a potential adjuvant for NSCLC patients during erlotinib treatment.
Keywords: TG101348; cancer therapy; drug resistance; erlotinib; non-small cell lung cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Curcumin lowers erlotinib resistance in non-small cell lung carcinoma cells with mutated EGF receptor.Oncol Res. 2013;21(3):137-44. doi: 10.3727/096504013X13832473330032. Oncol Res. 2013. PMID: 24512728
-
Combined Erlotinib and Cetuximab overcome the acquired resistance to epidermal growth factor receptors tyrosine kinase inhibitor in non-small-cell lung cancer.J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2012 Dec;138(12):2069-77. doi: 10.1007/s00432-012-1291-2. Epub 2012 Jul 22. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2012. PMID: 22821179 Free PMC article.
-
Chloroquine in combination with aptamer-modified nanocomplexes for tumor vessel normalization and efficient erlotinib/Survivin shRNA co-delivery to overcome drug resistance in EGFR-mutated non-small cell lung cancer.Acta Biomater. 2018 Aug;76:257-274. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2018.06.034. Epub 2018 Jun 28. Acta Biomater. 2018. PMID: 29960010
-
Advances in targeting EGFR allosteric site as anti-NSCLC therapy to overcome the drug resistance.Pharmacol Rep. 2020 Aug;72(4):799-813. doi: 10.1007/s43440-020-00131-0. Epub 2020 Jul 14. Pharmacol Rep. 2020. PMID: 32666476 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multimodal omics analysis of the EGFR signaling pathway in non-small cell lung cancer and emerging therapeutic strategies.Oncol Res. 2025 May 29;33(6):1363-1376. doi: 10.32604/or.2025.059311. eCollection 2025. Oncol Res. 2025. PMID: 40486879 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Single B Cell Gene Co-Expression Networks Implicated in Prognosis, Proliferation, and Therapeutic Responses in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Bulk Tumors.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Jun 25;14(13):3123. doi: 10.3390/cancers14133123. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35804895 Free PMC article.
-
Synergistic Anti-Cancer Activity of Melittin and Erlotinib in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Mar 22;26(7):2903. doi: 10.3390/ijms26072903. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40243485 Free PMC article.
-
Matrine increases the inhibitory effects of afatinib on H1975 cells via the IL‑6/JAK1/STAT3 signaling pathway.Mol Med Rep. 2017 Sep;16(3):2733-2739. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2017.6865. Epub 2017 Jun 27. Mol Med Rep. 2017. PMID: 28656237 Free PMC article.
-
Unraveling the complexity of STAT3 in cancer: molecular understanding and drug discovery.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2024 Jan 20;43(1):23. doi: 10.1186/s13046-024-02949-5. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2024. PMID: 38245798 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Polo-like kinase 1 inhibition diminishes acquired resistance to epidermal growth factor receptor inhibition in non-small cell lung cancer with T790M mutations.Oncotarget. 2016 Jul 26;7(30):47998-48010. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.10332. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27384992 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E, Forman D. Global cancer statistics. CA: a cancer journal for clinicians. 2011;61:69–90. - PubMed
-
- Weiss JM, Villaruz LC, Socinski MA, Ivanova A, Grilley-Olson J, Dhruva N, Stinchcombe TE. A single-arm phase II trial of pazopanib in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer with non-squamous histology with disease progression on bevacizumab containing therapy. Lung Cancer. 2014;86:288–290. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Shi Y, Au JS, Thongprasert S, Srinivasan S, Tsai CM, Khoa MT, Heeroma K, Itoh Y, Cornelio G, Yang PC. A prospective, molecular epidemiology study of EGFR mutations in Asian patients with advanced non-small-cell lung cancer of adenocarcinoma histology (PIONEER) Journal of thoracic oncology : official publication of the International Association for the Study of Lung Cancer. 2014;9:154–162. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hirsch FR, Jänne PA, Eberhardt WE, Cappuzzo F, Thatcher N, Pirker R, Choy H, Kim ES, Paz-Ares L, Gandara DR. Epidermal growth factor receptor inhibition in lung cancer: status 2012. Journal of Thoracic Oncology. 2013;8:373–384. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

