Outcomes and costs of surgical treatments of necrotizing enterocolitis
- PMID: 25869373
- PMCID: PMC4411777
- DOI: 10.1542/peds.2014-1058
Outcomes and costs of surgical treatments of necrotizing enterocolitis
Abstract
Background and objectives: Despite previous studies demonstrating no difference in mortality or morbidity, the various surgical approaches for necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC) in infants have not been evaluated economically. Our goal was to compare total in-hospital cost and mortality by using propensity score-matched infants treated with peritoneal drainage alone, peritoneal drainage followed by laparotomy, or laparotomy alone for surgical NEC.
Methods: Utilizing the California OSHPD Linked Birth File Dataset, 1375 infants with surgical NEC between 1999 and 2007 were retrospectively propensity score matched according to intervention type. Total in-hospital costs were converted from longitudinal patient charges. A multivariate mixed effects model compared adjusted costs and mortality between groups.
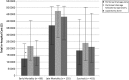
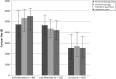
Results: Successful propensity score matching was performed with 699 infants (peritoneal drainage, n = 101; peritoneal drainage followed by laparotomy, n = 172; and laparotomy, n = 426). Average adjusted cost for peritoneal drainage followed by laparotomy was $398,173 (95% confidence interval [CI]: 287,784-550,907), which was more than for peritoneal drainage ($276,076 [95% CI: 196,238-388,394]; P = .004) and similar to laparotomy ($341,911 [95% CI: 251,304-465,186]; P = .08). Adjusted mortality was highest after peritoneal drainage (56% [95% CI: 34-75]) versus peritoneal drainage followed by laparotomy (35% [95% CI: 19-56]; P = .01) and laparotomy (29% [95% CI: 19-56]; P < .001). Mortality for peritoneal drainage was similar to laparotomy.
Conclusions: Propensity score-matched analysis of surgical NEC treatment found that peritoneal drainage followed by laparotomy was associated with decreased mortality compared with peritoneal drainage alone but at significantly increased costs.
Keywords: cost analysis; mortality; necrotizing enterocolitis; prematurity; surgery.
Copyright © 2015 by the American Academy of Pediatrics.
Figures
References
-
- Eicher C, Seitz G, Bevot A, et al. . Surgical management of extremely low birth weight infants with neonatal bowel perforation: a single-center experience and a review of the literature. Neonatology. 2012;101(4):285–292 - PubMed
-
- Arnold M, Moore SW, Sidler D, Kirsten GF. Long-term outcome of surgically managed necrotizing enterocolitis in a developing country. Pediatr Surg Int. 2010;26(4):355–360 - PubMed
-
- Fitzgibbons SC, Ching Y, Yu D, et al. . Mortality of necrotizing enterocolitis expressed by birth weight categories. J Pediatr Surg. 2009;44(6):1072–1075, discussion 1075–1076 - PubMed
-
- Zhang Y, Ortega G, Camp M, Osen H, Chang DC, Abdullah F. Necrotizing enterocolitis requiring surgery: outcomes by intestinal location of disease in 4371 infants. J Pediatr Surg. 2011;46(8):1475–1481 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

