A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial to evaluate the efficacy, safety, and tolerability of prucalopride in men with chronic constipation
- PMID: 25869393
- PMCID: PMC4424376
- DOI: 10.1038/ajg.2015.115
A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial to evaluate the efficacy, safety, and tolerability of prucalopride in men with chronic constipation
Abstract
Objectives: Prucalopride is effective at alleviating symptoms of chronic constipation in women. The aim of this study was to assess the efficacy of 12 weeks of prucalopride treatment compared with placebo in men with chronic constipation.
Methods: This was a multicenter, stratified, randomized, parallel-group, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 study (ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT01147926). The primary end point was the proportion of patients with a mean of three or more spontaneous complete bowel movements (SCBMs) per week across the treatment period. Efficacy end points were assessed using daily electronic diaries, global assessment of the severity of constipation and efficacy of treatment, and Patient Assessment of Constipation-Symptoms (PAC-SYM) and Patient Assessment of Constipation-Quality of Life (PAC-QOL) questionnaires.
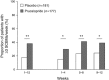
Results: In total, 374 patients were enrolled in the study. Significantly more patients achieved a mean of three or more SCBMs per week in the prucalopride group (37.9%) than in the placebo group (17.7%, P<0.0001). The proportion of patients rating their constipation treatment as "quite a bit" to "extremely" effective at the final on-treatment visit was 46.7 and 30.4% in the prucalopride and placebo groups, respectively. The difference between treatment groups was statistically significant (P<0.0001). The proportion of patients with an improvement of at least 1 point in PAC-QOL satisfaction subscale score was 52.7 and 38.8% in the prucalopride and placebo groups, respectively (P=0.0035). Prucalopride had a good safety profile and was well tolerated.
Conclusions: Prucalopride is effective, has a good safety profile, and is well tolerated for the treatment of men with chronic constipation.
Figures

References
-
- Johanson JF, Kralstein J. Chronic constipation: a survey of the patient perspective. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2007;25:599–608. - PubMed
-
- Herz MJ, Kahan E, Zalevski S, et al. Constipation: a different entity for patients and doctors. Fam Pract. 1996;13:156–9. - PubMed
-
- Longstreth GF, Thompson WG, Chey WD, et al. Functional bowel disorders. Gastroenterology. 2006;130:1480–91. - PubMed
-
- Suares NC, Ford AC. Prevalence of, and risk factors for, chronic idiopathic constipation in the community: systematic review and meta-analysis. Am J Gastroenterol. 2011;106:1582–91. - PubMed
-
- Wald A, Scarpignato C, Mueller-Lissner S, et al. A multinational survey of prevalence and patterns of laxative use among adults with self-defined constipation. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2008;28:917–30. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

