Looking beyond the induction of Th2 responses to explain immunomodulation by helminths
- PMID: 25869527
- PMCID: PMC4425638
- DOI: 10.1111/pim.12194
Looking beyond the induction of Th2 responses to explain immunomodulation by helminths
Abstract
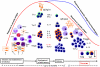
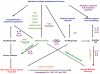
Although helminth infections are characteristically associated with Th2-mediated responses that include the production of the prototypical cytokines IL-4, IL-5 and IL-13 by CD4(+) cells, the production of IgE, peripheral blood eosinophilia and mucus production in localized sites, these responses are largely attenuated when helminth infections become less acute. This modulation of the immune response that occurs with chronic helminth infection is often induced by molecules secreted by helminth parasites, by non-Th2 regulatory CD4(+) cells, and by nonclassical B cells, macrophages and dendritic cells. This review will focus on those parasite- and host-mediated mechanisms underlying the modulated T-cell response that occurs as the default in chronic helminth infections.
Keywords: IL-10; IgE; IgG4; Th2 responses; alternatively activated macrophages; dendritic cells; helminths; immune modulation; innate lymphoid cells; regulatory B cells; regulatory T cells.
Published 2015. This article is a U.S. Government work and is in the public domain in the USA.
Figures
References
-
- Allen JE, Maizels RM. Diversity and dialogue in immunity to helminths. Nat Rev Immunol. 2011;11:375–388. - PubMed
-
- Harnett W, Harnett MM. Lymphocyte hyporesponsiveness during filarial nematode infection. Parasite Immunol. 2008;30:447–453. - PubMed
-
- Wammes LJ, Hamid F, Wiria AE, et al. Regulatory T cells in human geohelminth infection suppress immune responses to BCG and Plasmodium falciparum. Eur J Immunol. 2010;40:437–442. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

