Recent insights into the cellular biology of atherosclerosis
- PMID: 25869663
- PMCID: PMC4395483
- DOI: 10.1083/jcb.201412052
Recent insights into the cellular biology of atherosclerosis
Abstract
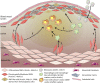
Atherosclerosis occurs in the subendothelial space (intima) of medium-sized arteries at regions of disturbed blood flow and is triggered by an interplay between endothelial dysfunction and subendothelial lipoprotein retention. Over time, this process stimulates a nonresolving inflammatory response that can cause intimal destruction, arterial thrombosis, and end-organ ischemia. Recent advances highlight important cell biological atherogenic processes, including mechanotransduction and inflammatory processes in endothelial cells, origins and contributions of lesional macrophages, and origins and phenotypic switching of lesional smooth muscle cells. These advances illustrate how in-depth mechanistic knowledge of the cellular pathobiology of atherosclerosis can lead to new ideas for therapy.
© 2015 Tabas et al.
Figures


References
-
- Alexander M.R., Moehle C.W., Johnson J.L., Yang Z., Lee J.K., Jackson C.L., and Owens G.K.. 2012. Genetic inactivation of IL-1 signaling enhances atherosclerotic plaque instability and reduces outward vessel remodeling in advanced atherosclerosis in mice. J. Clin. Invest. 122:70–79 10.1172/JCI43713 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- HL118826/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL107497/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- AG032443/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- HL087867/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R37 HL057353/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL107497/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL121008/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R44 HL118826/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R41 HL118826/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL075662/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL057353/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL087867/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL075662/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL057353/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL121008/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG032443/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

