Deletion of adenosine A2A receptors from astrocytes disrupts glutamate homeostasis leading to psychomotor and cognitive impairment: relevance to schizophrenia
- PMID: 25869810
- PMCID: PMC4714966
- DOI: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2015.02.026
Deletion of adenosine A2A receptors from astrocytes disrupts glutamate homeostasis leading to psychomotor and cognitive impairment: relevance to schizophrenia
Abstract
Background: Adenosine A2A receptors (A2AR) modulate dopamine and glutamate signaling and thereby may influence some of the psychomotor and cognitive processes associated with schizophrenia. Because astroglial A2AR regulate the availability of glutamate, we hypothesized that they might play an unprecedented role in some of the processes leading to the development of schizophrenia, which we investigated using a mouse line with a selective deletion of A2AR in astrocytes (Gfa2-A2AR knockout [KO] mice].
Methods: We examined Gfa2-A2AR KO mice for behaviors thought to recapitulate some features of schizophrenia, namely enhanced MK-801 psychomotor response (positive symptoms) and decreased working memory (cognitive symptoms). In addition, we probed for neurochemical alterations in the glutamatergic circuitry, evaluating glutamate uptake and release and the levels of key proteins defining glutamatergic signaling (glutamate transporter-I [GLT-I], N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors [NMDA-R] and α-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid receptors [AMPA-R]) to provide a mechanistic understanding of the phenotype encountered.
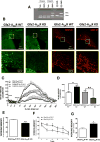
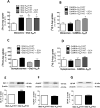
Results: We show that Gfa2-A2AR KO mice exhibited enhanced MK-801 psychomotor response and decreased working memory; this was accompanied by a disruption of glutamate homeostasis characterized by aberrant GLT-I activity, increased presynaptic glutamate release, NMDA-R 2B subunit upregulation, and increased internalization of AMPA-R. Accordingly, selective GLT-I inhibition or blockade of GluR1/2 endocytosis prevented the psychomotor and cognitive phenotypes in Gfa2-A2AR KO mice, namely in the nucleus accumbens.
Conclusions: These results show that the dysfunction of astrocytic A2AR, by controlling GLT-I activity, triggers an astrocyte-to-neuron wave of communication resulting in disrupted glutamate homeostasis, thought to underlie several endophenotypes relevant to schizophrenia.
Keywords: A(2A)R; Adenosine; Astrocytes; GLT-I; NMDA-R; Schizophrenia.
Copyright © 2015. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors declare no biomedical financial interests or potential conflicts of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Antagonistic interaction between adenosine A2A receptors and Na+/K+-ATPase-α2 controlling glutamate uptake in astrocytes.J Neurosci. 2013 Nov 20;33(47):18492-502. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1828-13.2013. J Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 24259572 Free PMC article.
-
Astrocytic adenosine A2A receptors control the amyloid-β peptide-induced decrease of glutamate uptake.J Alzheimers Dis. 2012;31(3):555-67. doi: 10.3233/JAD-2012-120469. J Alzheimers Dis. 2012. PMID: 22647260
-
Knocking out the glial glutamate transporter GLT-1 reduces glutamate uptake but does not affect hippocampal glutamate dynamics in early simulated ischaemia.Eur J Neurosci. 2002 Jan;15(2):308-14. doi: 10.1046/j.0953-816x.2001.01861.x. Eur J Neurosci. 2002. PMID: 11849297
-
GLT-1: The elusive presynaptic glutamate transporter.Neurochem Int. 2016 Sep;98:19-28. doi: 10.1016/j.neuint.2016.04.010. Epub 2016 Apr 26. Neurochem Int. 2016. PMID: 27129805 Free PMC article. Review.
-
[Role of astrocytes in alterations of glutamatergic neurotransmission in schizophrenia].Zh Nevrol Psikhiatr Im S S Korsakova. 2015;115(1):110-117. doi: 10.17116/jnevro201511511110-117. Zh Nevrol Psikhiatr Im S S Korsakova. 2015. PMID: 25945378 Review. Russian.
Cited by
-
Allosteric Modulation of Adenosine A2A Receptors as a New Therapeutic Avenue.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Feb 14;23(4):2101. doi: 10.3390/ijms23042101. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35216213 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Neuroprotection by caffeine in the MPTP model of parkinson's disease and its dependence on adenosine A2A receptors.Neuroscience. 2016 May 13;322:129-37. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2016.02.035. Epub 2016 Feb 22. Neuroscience. 2016. PMID: 26905951 Free PMC article.
-
40 Hz light flickering facilitates the glymphatic flow via adenosine signaling in mice.Cell Discov. 2024 Aug 6;10(1):81. doi: 10.1038/s41421-024-00701-z. Cell Discov. 2024. PMID: 39103336 Free PMC article.
-
Astrocytes and Adenosine A2A Receptors: Active Players in Alzheimer's Disease.Front Neurosci. 2021 May 13;15:666710. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2021.666710. eCollection 2021. Front Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 34054416 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Comorbidities in Neurology: Is adenosine the common link?Neuropharmacology. 2015 Oct;97:18-34. doi: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2015.04.031. Epub 2015 May 13. Neuropharmacology. 2015. PMID: 25979489 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ross CA, Margolis RL, Reading SA, Pletnikov M, Coyle JT. Neurobiology of schizophrenia. Neuron. 2006;5:139–153. - PubMed
-
- Van Snellenberg JX. Working memory and long-term memory deficits in schizophrenia: Is there a common substrate? Psychiatry Res. 2009;174:89–96. - PubMed
-
- Kristiansen LV, Huerta I, Beneyto M, Meador-Woodruff JH. NMDA receptors and schizophrenia. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2007;7:48–55. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

