Genetic Analysis of Connective Tissue Growth Factor as an Effector of Transforming Growth Factor β Signaling and Cardiac Remodeling
- PMID: 25870108
- PMCID: PMC4438237
- DOI: 10.1128/MCB.00199-15
Genetic Analysis of Connective Tissue Growth Factor as an Effector of Transforming Growth Factor β Signaling and Cardiac Remodeling
Abstract
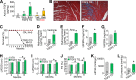
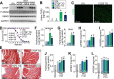
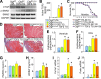
The matricellular secreted protein connective tissue growth factor (CTGF) is upregulated in response to cardiac injury or with transforming growth factor β (TGF-β) stimulation, where it has been suggested to function as a fibrotic effector. Here we generated transgenic mice with inducible heart-specific CTGF overexpression, mice with heart-specific expression of an activated TGF-β mutant protein, mice with heart-specific deletion of Ctgf, and mice in which Ctgf was also deleted from fibroblasts in the heart. Remarkably, neither gain nor loss of CTGF in the heart affected cardiac pathology and propensity toward early lethality due to TGF-β overactivation in the heart. Also, neither heart-specific Ctgf deletion nor CTGF overexpression altered cardiac remodeling and function with aging or after multiple acute stress stimuli. Cardiac fibrosis was also unchanged by modulation of CTGF levels in the heart with aging, pressure overload, agonist infusion, or TGF-β overexpression. However, CTGF mildly altered the overall cardiac response to TGF-β when pressure overload stimulation was applied. CTGF has been proposed to function as a critical TGF-β effector in underlying tissue remodeling and fibrosis throughout the body, although our results suggest that CTGF is of minimal importance and is an unlikely therapeutic vantage point for the heart.
Copyright © 2015, American Society for Microbiology. All Rights Reserved.
Figures



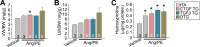

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
