Desformylflustrabromine (dFBr) and [3H]dFBr-Labeled Binding Sites in a Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor
- PMID: 25870334
- PMCID: PMC4468644
- DOI: 10.1124/mol.115.098913
Desformylflustrabromine (dFBr) and [3H]dFBr-Labeled Binding Sites in a Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor
Erratum in
-
Correction to "Desformylflustrabromine (dFBr) and [3H]dFBr-Labeled Binding Sites in a Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor".Mol Pharmacol. 2016 Jan;89(1):141. doi: 10.1124/mol.115.098913err. Mol Pharmacol. 2016. PMID: 26655585 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
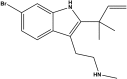
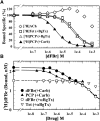
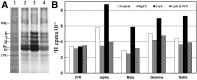
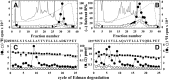
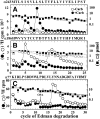
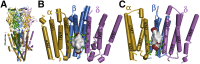
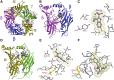
Desformylflustrabromine (dFBr) is a positive allosteric modulator (PAM) of α4β2 and α2β2 nAChRs that, at concentrations >1 µM, also inhibits these receptors and α7 nAChRs. However, its interactions with muscle-type nAChRs have not been characterized, and the locations of its binding site(s) in any nAChR are not known. We report here that dFBr inhibits human muscle (αβεδ) and Torpedo (αβγδ) nAChR expressed in Xenopus oocytes with IC50 values of ∼ 1 μM. dFBr also inhibited the equilibrium binding of ion channel blockers to Torpedo nAChRs with higher affinity in the nAChR desensitized state ([(3)H]phencyclidine; IC50 = 4 μM) than in the resting state ([(3)H]tetracaine; IC50 = 60 μM), whereas it bound with only very low affinity to the ACh binding sites ([(3)H]ACh, IC50 = 1 mM). Upon irradiation at 312 nm, [(3)H]dFBr photoincorporated into amino acids within the Torpedo nAChR ion channel with the efficiency of photoincorporation enhanced in the presence of agonist and the agonist-enhanced photolabeling inhibitable by phencyclidine. In the presence of agonist, [(3)H]dFBr also photolabeled amino acids in the nAChR extracellular domain within binding pockets identified previously for the nonselective nAChR PAMs galantamine and physostigmine at the canonical α-γ interface containing the transmitter binding sites and at the noncanonical δ-β subunit interface. These results establish that dFBr inhibits muscle-type nAChR by binding in the ion channel and that [(3)H]dFBr is a photoaffinity probe with broad amino acid side chain reactivity.
Copyright © 2015 by The American Society for Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics.
Figures




References
-
- Arevalo E, Chiara DC, Forman SA, Cohen JB, Miller KW. (2005) Gating-enhanced accessibility of hydrophobic sites within the transmembrane region of the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor’s δ-subunit. A time-resolved photolabeling study. J Biol Chem 280:13631–13640. - PubMed
-
- Arias HR. (2010) Positive and negative modulation of nicotinic receptors. Adv Protein Chem Struct Biol 80:153–203. - PubMed
-
- Bertrand D, Bertrand S, Cassar S, Gubbins E, Li J, Gopalakrishnan M. (2008) Positive allosteric modulation of the α7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor: ligand interactions with distinct binding sites and evidence for a prominent role of the M2-M3 segment. Mol Pharmacol 74:1407–1416. - PubMed
-
- Bertrand D, Gopalakrishnan M. (2007) Allosteric modulation of nicotinic acetylcholine receptors. Biochem Pharmacol 74:1155–1163. - PubMed
-
- Blanton MP, Cohen JB. (1994) Identifying the lipid-protein interface of the Torpedo nicotinic acetylcholine receptor: secondary structure implications. Biochemistry 33:2859–2872. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

