Nutrient requirements and growth physiology of the photoheterotrophic Acidobacterium, Chloracidobacterium thermophilum
- PMID: 25870589
- PMCID: PMC4376005
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2015.00226
Nutrient requirements and growth physiology of the photoheterotrophic Acidobacterium, Chloracidobacterium thermophilum
Abstract
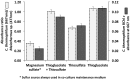
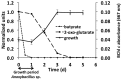
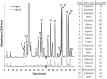
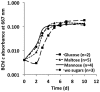
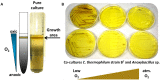
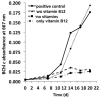
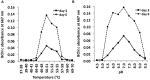
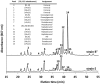
A novel thermophilic, microaerophilic, anoxygenic, and chlorophototrophic member of the phylum Acidobacteria, Chloracidobacterium thermophilum strain B(T), was isolated from a cyanobacterial enrichment culture derived from microbial mats associated with Octopus Spring, Yellowstone National Park, Wyoming. C. thermophilum is strictly dependent on light and oxygen and grows optimally as a photoheterotroph at irradiance values between 20 and 50 μmol photons m(-2) s(-1). C. thermophilum is unable to synthesize branched-chain amino acids (AAs), l-lysine, and vitamin B12, which are required for growth. Although the organism lacks genes for autotrophic carbon fixation, bicarbonate is also required. Mixtures of other AAs and 2-oxoglutarate stimulate growth. As suggested from genomic sequence data, C. thermophilum requires a reduced sulfur source such as thioglycolate, cysteine, methionine, or thiosulfate. The organism can be grown in a defined medium at 51(∘)C (Topt; range 44-58(∘)C) in the pH range 5.5-9.5 (pHopt = ∼7.0). Using the defined growth medium and optimal conditions, it was possible to isolate new C. thermophilum strains directly from samples of hot spring mats in Yellowstone National Park, Wyoming. The new isolates differ from the type strain with respect to pigment composition, morphology in liquid culture, and temperature adaptation.
Keywords: Acidobacteria; anoxygenic photosynthesis; bacteriochlorophyll; photoheterotroph; thermophile.
Figures




References
-
- Allewalt J. P., Bateson M. M., Revsbech N.-P., Slack K., Ward D. M. (2006). Effect of temperature and light on growth and photosynthesis of Synechococcus isolates typical of those predominating in the Octopus spring microbial mat community of Yellowstone National Park. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 72 544–550 10.1128/AEM.72.1.544-550.2006 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

