Structure of a TLR4-interacting SPA4 peptide
- PMID: 25870755
- PMCID: PMC4392768
- DOI: 10.1039/C4RA16731G
Structure of a TLR4-interacting SPA4 peptide
Abstract
We have recently identified a Toll-like receptor (TLR4)-interacting SPA4 peptide encoding amino acids: GDFRYSDGTPVNYTNWYRGE, a shorter region of human surfactant protein-A (SP-A). The SPA4 peptide suppressed lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation (JPET 2011, Innate Immun 2013). In this report, we examined the structure of synthetic SPA4 peptide in solution by circular dichroism (CD) and nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) spectroscopy. The CD analysis revealed that the SPA4 peptide is composed of ∼35% beta sheet and <5% alpha helix. We used solution NMR to solve the structure of the SPA4 peptide. We calculated NMR structures using Nuclear Overhauser Enhancement (NOE) distance restraints. The superposition of the low energy structures indicated that the central 6-14 amino acids "SDGTPVNYT" of the 20mer SPA4 peptide form a turn, and amino acids on either side (GDFRY and NWYRGE) conform to flexible arms. Furthermore, thermal denaturation experiments demonstrated the structural flexibility of the peptide. The NMR structures of the SPA4 peptide align well with the homologous region within the available structure of rat SP-A and a computationally-docked model of SP-A-TLR4-MD2 protein complex. Together, our results support the structural adaptability of SPA4 peptide for binding to TLR4.
Keywords: Surfactant protein-A-derived peptide; Toll-like receptor-4; structure.
Figures




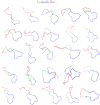



References
-
- King RJ. Pulmonary surfactant. J Appl Physiol Respir Environ Exerc Physiol. 1982;53(1):1–8. - PubMed
-
- Wright JR, Borron P, Brinker KG, Folz RJ. Surfactant Protein A: regulation of innate and adaptive immune responses in lung inflammation. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2001;24(5):513–7. - PubMed
-
- Gardai SJ, Xiao YQ, Dickinson M, Nick JA, Voelker DR, Greene KE, et al. By binding SIRPalpha or calreticulin/CD91, lung collectins act as dual function surveillance molecules to suppress or enhance inflammation. Cell. 2003;115(1):13–23. - PubMed
-
- Tino MJ, Wright JR. Glycoprotein-340 binds surfactant protein-A (SP-A) and stimulates alveolar macrophage migration in an SP-A-independent manner. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 1999;20(4):759–68. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
