Overview of clinicopathologic features of ALK-rearranged lung adenocarcinoma and current diagnostic testing for ALK rearrangement
- PMID: 25870797
- PMCID: PMC4384218
- DOI: 10.3978/j.issn.2218-6751.2014.12.02
Overview of clinicopathologic features of ALK-rearranged lung adenocarcinoma and current diagnostic testing for ALK rearrangement
Abstract
Patients with non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) who harbor anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) gene rearrangements can derive significant clinical benefit from ALK tyrosine kinase inhibitor. Accurate patient identification is absolutely crucial for successful using ALK inhibitor treatment. However, lung cancer patients with ALK gene rearrangement after ALK inhibitor therapy eventually develop acquired resistance to treatment. In this review, the authors summarize the clinicopathologic features of ALK-rearranged NSCLC and the pros and cons of current diagnostic testing. In addition, we discuss the current diagnostic flow of ALK testing and consideration of rebiopsy sample during disease progression in patients treated by ALK inhibitors.
Keywords: Anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK) gene rearrangement; fluorescent in situ hybridization (FISH); histology; immunohistochemistry (IHC); non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC).
Figures
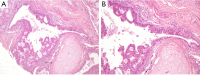
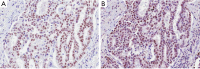
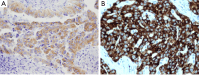
References
-
- Soda M, Choi YL, Enomoto M, et al. Identification of the transforming EML4-ALK fusion gene in non-small-cell lung cancer. Nature 2007;448:561-6. - PubMed
-
- Bang YJ. Treatment of ALK-positive non-small cell lung cancer. Arch Pathol Lab Med 2012;136:1201-4. - PubMed
-
- Inamura K, Takeuchi K, Togashi Y, et al. EML4-ALK fusion is linked to histological characteristics in a subset of lung cancers. J Thorac Oncol 2008;3:13-7. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
