Young age at start of antiretroviral therapy and negative HIV antibody results in HIV-infected children when suppressed
- PMID: 25870988
- PMCID: PMC4538987
- DOI: 10.1097/QAD.0000000000000677
Young age at start of antiretroviral therapy and negative HIV antibody results in HIV-infected children when suppressed
Abstract
Background: Negative results on standard HIV antibody tests have been described among HIV-infected children suppressed on antiretroviral therapy (ART) started early in life. Here, we describe the frequency and predictors of this phenomenon in a well characterized cohort of treated children.
Methods: We selected samples from 103 HIV-infected children who started ART 14 months of age or less and from 122 children who started 6 months of age or less followed as part of two sequential clinical trials in Johannesburg, South Africa. Children had attained viral suppression on ART and had received ART for between 3 and 6.4 years (mean 4.3 years) when tested for HIV antibody using a standard ELISA (Genescreen HIV1/2 version 2; Bio-rad).
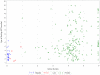
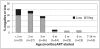
Results: Only children 6 months of age or less when ART was started had negative antibody results when tested after suppression on ART several years later. Negative or low-positive antibody results were observed in 40.0, 37.0 and 27.8% of children starting ART less than 2 months of age, or starting during month 2 or 3, respectively. This dropped to 5.9, 3.5 and 5.3% if ART was started during month 4, 5 and 6, respectively. Higher CD4 percentage prior to ART initiation and no recorded intermittent viremia also predicted negative antibody results.
Conclusion: Testing negative on standard HIV antibody tests occurs fairly commonly among HIV-infected children who started ART 3 months of age or less and are virally suppressed. It would be prudent in clinical practice to avoid HIV antibody tests among virally suppressed, early-treated children to prevent unnecessary confusion.
Figures
References
-
- Creek TL, Sherman GG, Nkengasong J, et al. Infant human immunodeficiency virus diagnosis in resource-limited settings: issues, technologies, and country experiences. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2007;197:S64–71. - PubMed
-
- Van der Linden D, Hainaut M, Goetghebuer T, et al. Effectiveness of early initiation of protease inhibitor-sparing antiretroviral regimen in human immunodeficiency virus-1 vertically infected infants. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2007;26:359–61. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

