AXL mediates resistance to PI3Kα inhibition by activating the EGFR/PKC/mTOR axis in head and neck and esophageal squamous cell carcinomas
- PMID: 25873175
- PMCID: PMC4398915
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ccell.2015.03.010
AXL mediates resistance to PI3Kα inhibition by activating the EGFR/PKC/mTOR axis in head and neck and esophageal squamous cell carcinomas
Abstract
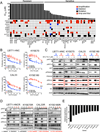
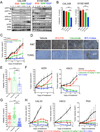
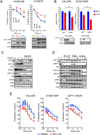
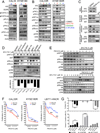
Phosphoinositide-3-kinase (PI3K)-α inhibitors have shown clinical activity in squamous cell carcinomas (SCCs) of head and neck (H&N) bearing PIK3CA mutations or amplification. Studying models of therapeutic resistance, we have observed that SCC cells that become refractory to PI3Kα inhibition maintain PI3K-independent activation of the mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR). This persistent mTOR activation is mediated by the tyrosine kinase receptor AXL. AXL is overexpressed in resistant tumors from both laboratory models and patients treated with the PI3Kα inhibitor BYL719. AXL dimerizes with and phosphorylates epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), resulting in activation of phospholipase Cγ (PLCγ)-protein kinase C (PKC), which, in turn, activates mTOR. Combined treatment with PI3Kα and either EGFR, AXL, or PKC inhibitors reverts this resistance.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
J.B., D.J. and N.R. have consulted for Novartis Pharmaceuticals. A.H., Q.S., J.J.Y., R.D., Y.C., A.T., H.W., J.L., and M.L. are full-time employees of Novartis Pharmaceuticals.
Figures



Similar articles
-
TAM family receptors in conjunction with MAPK signalling are involved in acquired resistance to PI3Kα inhibition in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2020 Oct 15;39(1):217. doi: 10.1186/s13046-020-01713-9. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2020. PMID: 33059733 Free PMC article.
-
Repression of AXL expression by AP-1/JNK blockage overcomes resistance to PI3Ka therapy.JCI Insight. 2019 Mar 12;5(8):e125341. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.125341. JCI Insight. 2019. PMID: 30860495 Free PMC article.
-
AXL mediates resistance to cetuximab therapy.Cancer Res. 2014 Sep 15;74(18):5152-64. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-14-0294. Epub 2014 Aug 18. Cancer Res. 2014. PMID: 25136066 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Pathways: AXL, a Membrane Receptor Mediator of Resistance to Therapy.Clin Cancer Res. 2016 Mar 15;22(6):1313-7. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-15-1458. Epub 2016 Jan 13. Clin Cancer Res. 2016. PMID: 26763248 Free PMC article. Review.
-
PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling as a molecular target in head and neck cancer.Biochem Pharmacol. 2020 Feb;172:113729. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2019.113729. Epub 2019 Nov 27. Biochem Pharmacol. 2020. PMID: 31785230 Review.
Cited by
-
Emerging roles for the GPI-anchored tumor suppressor OPCML in cancers.Cancer Gene Ther. 2021 Feb;28(1-2):18-26. doi: 10.1038/s41417-020-0187-6. Epub 2020 Jun 29. Cancer Gene Ther. 2021. PMID: 32595215 Review.
-
Comparative genomic analysis of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma and adenocarcinoma: New opportunities towards molecularly targeted therapy.Acta Pharm Sin B. 2022 Mar;12(3):1054-1067. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2021.09.028. Epub 2021 Sep 30. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2022. PMID: 35530133 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Receptor Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor Sensitivity Prediction Model Identifies AXL Dependency in Leukemia.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Feb 14;24(4):3830. doi: 10.3390/ijms24043830. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36835239 Free PMC article.
-
Dihydroartemisinin inhibits prostate cancer via JARID2/miR-7/miR-34a-dependent downregulation of Axl.Oncogenesis. 2019 Feb 19;8(3):14. doi: 10.1038/s41389-019-0122-6. Oncogenesis. 2019. PMID: 30783079 Free PMC article.
-
Osimertinib and dihydroartemisinin: a novel drug combination targeting head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.Ann Transl Med. 2019 Nov;7(22):651. doi: 10.21037/atm.2019.10.80. Ann Transl Med. 2019. PMID: 31930052 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Akagi I, Miyashita M, Makino H, Nomura T, Hagiwara N, Takahashi K, Cho K, Mishima T, Ishibashi O, Ushijima T, et al. Overexpression of PIK3CA is associated with lymph node metastasis in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Oncol. 2009;34:767–775. - PubMed
-
- Baselga J, Trigo JM, Bourhis J, Tortochaux J, Cortes-Funes H, Hitt R, Gascon P, Amellal N, Harstrick A, Eckardt A. Phase II multicenter study of the antiepidermal growth factor receptor monoclonal antibody cetuximab in combination with platinum-based chemotherapy in patients with platinum-refractory metastatic and/or recurrent squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck. J Clin Oncol. 2005;23:5568–5577. - PubMed
-
- Bonner JA, Harari PM, Giralt J, Azarnia N, Shin DM, Cohen RB, Jones CU, Sur R, Raben D, Jassem J, et al. Radiotherapy plus cetuximab for squamous-cell carcinoma of the head and neck. N Engl J Med. 2006;354:567–578. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

