Cystathionine β-synthase inhibition is a potential therapeutic approach to treatment of ischemic injury
- PMID: 25873304
- PMCID: PMC4397212
- DOI: 10.1177/1759091415578711
Cystathionine β-synthase inhibition is a potential therapeutic approach to treatment of ischemic injury
Abstract
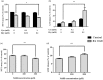
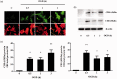
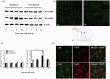
Hydrogen sulfide (H2S) has been reported to exacerbate stroke outcome in experimental models. Cystathionine β-synthase (CBS) has been implicated as the predominant H2S-producing enzyme in central nervous system. When SH-SY5Y cells were transfected to overexpress CBS, these cells were able to synthesize H2S when exposed to high levels of enzyme substrates but not substrate concentrations that may reflect normal physiological conditions. At the same time, these cells demonstrated exacerbated cell death when subjected to oxygen and glucose deprivation (OGD) together with high substrate concentrations, indicating that H2S production has a detrimental effect on cell survival. This effect could be abolished by CBS inhibition. The same effect was observed with primary astrocytes exposed to OGD and high substrates or sodium hydrosulfide. In addition, CBS was upregulated and activated by truncation in primary astrocytes subjected to OGD. When rats were subjected to permanent middle cerebral artery occlusion, CBS activation was also observed. These results imply that in acute ischemic conditions, CBS is upregulated and activated by truncation causing an increased production of H2S, which exacerbate the ischemic injuries. Therefore, CBS inhibition may be a viable approach to stroke treatment.
Keywords: cystathioine β-synthase; cysteine; homocysteine; hydrogen sulfide; oxygen glucose deprivation; stroke.
© The Author(s) 2015.
Figures




Similar articles
-
MiR-125b-5p is involved in oxygen and glucose deprivation injury in PC-12 cells via CBS/H2S pathway.Nitric Oxide. 2018 Aug 1;78:11-21. doi: 10.1016/j.niox.2018.05.004. Epub 2018 May 17. Nitric Oxide. 2018. PMID: 29777774
-
The cystathionine β-synthase/hydrogen sulfide pathway contributes to microglia-mediated neuroinflammation following cerebral ischemia.Brain Behav Immun. 2017 Nov;66:332-346. doi: 10.1016/j.bbi.2017.07.156. Epub 2017 Jul 24. Brain Behav Immun. 2017. PMID: 28751019
-
Excessive nNOS/NO/AMPK signaling activation mediated by the blockage of the CBS/H2S system contributes to oxygen‑glucose deprivation‑induced endoplasmic reticulum stress in PC12 cells.Int J Mol Med. 2017 Aug;40(2):549-557. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2017.3035. Epub 2017 Jun 21. Int J Mol Med. 2017. PMID: 28656194
-
Cystathionine-β-Synthase: Molecular Regulation and Pharmacological Inhibition.Biomolecules. 2020 Apr 30;10(5):697. doi: 10.3390/biom10050697. Biomolecules. 2020. PMID: 32365821 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of hydrogen sulfide in secondary neuronal injury.Neurochem Int. 2014 Jan;64:37-47. doi: 10.1016/j.neuint.2013.11.002. Epub 2013 Nov 14. Neurochem Int. 2014. PMID: 24239876 Review.
Cited by
-
Upregulation of cystathionine β-synthase and p70S6K/S6 in neonatal hypoxic ischemic brain injury.Brain Pathol. 2017 Jul;27(4):449-458. doi: 10.1111/bpa.12421. Epub 2016 Aug 28. Brain Pathol. 2017. PMID: 27465493 Free PMC article.
-
Sulfide catabolism ameliorates hypoxic brain injury.Nat Commun. 2021 May 25;12(1):3108. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-23363-x. Nat Commun. 2021. PMID: 34035265 Free PMC article.
-
Modulator of apoptosis-1 is a potential therapeutic target in acute ischemic injury.J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2019 Dec;39(12):2406-2418. doi: 10.1177/0271678X18794839. Epub 2018 Aug 22. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 2019. PMID: 30132384 Free PMC article.
-
CBS promoter hypermethylation increases the risk of hypertension and stroke.Clinics (Sao Paulo). 2019 Mar 21;74:e630. doi: 10.6061/clinics/2019/e630. Clinics (Sao Paulo). 2019. PMID: 30916171 Free PMC article.
-
The role of medical gas in stroke: an updated review.Med Gas Res. 2019 Oct-Dec;9(4):221-228. doi: 10.4103/2045-9912.273960. Med Gas Res. 2019. PMID: 31898607 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Beauchamp R. O., Jr., Bus J. S., Popp J. A., Boreiko C. J., Andjelkovich D. A. (1984) A critical review of the literature on hydrogen sulfide toxicity. Critical Reviews in Toxicology 13: 25–97. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
