Low-dose sevoflurane promotes hippocampal neurogenesis and facilitates the development of dentate gyrus-dependent learning in neonatal rats
- PMID: 25873307
- PMCID: PMC4720175
- DOI: 10.1177/1759091415575845
Low-dose sevoflurane promotes hippocampal neurogenesis and facilitates the development of dentate gyrus-dependent learning in neonatal rats
Abstract
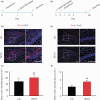
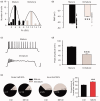
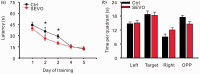
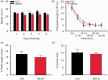
Huge body of evidences demonstrated that volatile anesthetics affect the hippocampal neurogenesis and neurocognitive functions, and most of them showed impairment at anesthetic dose. Here, we investigated the effect of low dose (1.8%) sevoflurane on hippocampal neurogenesis and dentate gyrus-dependent learning. Neonatal rats at postnatal day 4 to 6 (P4-6) were treated with 1.8% sevoflurane for 6 hours. Neurogenesis was quantified by bromodeoxyuridine labeling and electrophysiology recording. Four and seven weeks after treatment, the Morris water maze and contextual-fear discrimination learning tests were performed to determine the influence on spatial learning and pattern separation. A 6-hour treatment with 1.8% sevoflurane promoted hippocampal neurogenesis and increased the survival of newborn cells and the proportion of immature granular cells in the dentate gyrus of neonatal rats. Sevoflurane-treated rats performed better during the training days of the Morris water maze test and in contextual-fear discrimination learning test. These results suggest that a subanesthetic dose of sevoflurane promotes hippocampal neurogenesis in neonatal rats and facilitates their performance in dentate gyrus-dependent learning tasks.
Keywords: dentate gyrus; neonate; neurogenesis; pattern separation; sevoflurane; spatial learning.
© The Author(s) 2015.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Ketamine Affects the Neurogenesis of the Hippocampal Dentate Gyrus in 7-Day-Old Rats.Neurotox Res. 2016 Aug;30(2):185-98. doi: 10.1007/s12640-016-9615-7. Epub 2016 Mar 10. Neurotox Res. 2016. PMID: 26966008
-
From the Cover: Volatile Anesthetics Transiently Disrupt Neuronal Development in Neonatal Rats.Toxicol Sci. 2016 Dec;154(2):309-319. doi: 10.1093/toxsci/kfw164. Epub 2016 Aug 25. Toxicol Sci. 2016. PMID: 27562558
-
Sevoflurane affects neurogenesis after forebrain ischemia in rats.Anesth Analg. 2007 Apr;104(4):898-903. doi: 10.1213/01.ane.0000255730.73018.31. Anesth Analg. 2007. PMID: 17377103
-
Beyond anesthetic properties: the effects of isoflurane on brain cell death, neurogenesis, and long-term neurocognitive function.Anesth Analg. 2010 Feb;110(2):431-7. Anesth Analg. 2010. PMID: 25508825 Review.
-
Morris Water Maze and Contextual Fear Conditioning Tasks to Evaluate Cognitive Functions Associated With Adult Hippocampal Neurogenesis.Front Neurosci. 2022 Jan 3;15:782947. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2021.782947. eCollection 2021. Front Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35046769 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Dose-dependent effects of sevoflurane exposure during early lifetime on apoptosis in hippocampus and neurocognitive outcomes in Sprague-Dawley rats.Int J Physiol Pathophysiol Pharmacol. 2016 Sep 30;8(3):111-119. eCollection 2016. Int J Physiol Pathophysiol Pharmacol. 2016. PMID: 27785338 Free PMC article.
-
Exposure to Sevoflurane Affects the Development of Parvalbumin Interneurons in the Main Olfactory Bulb in Mice.Front Neuroanat. 2016 Jun 24;10:72. doi: 10.3389/fnana.2016.00072. eCollection 2016. Front Neuroanat. 2016. PMID: 27445710 Free PMC article.
-
Neurogenesis and developmental anesthetic neurotoxicity.Neurotoxicol Teratol. 2017 Mar-Apr;60:33-39. doi: 10.1016/j.ntt.2016.10.001. Epub 2016 Oct 14. Neurotoxicol Teratol. 2017. PMID: 27751818 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Repeated 2% sevoflurane administration in 7‑ and 60-day-old rats : Neurotoxicity and neurocognitive dysfunction.Anaesthesist. 2017 Nov;66(11):850-857. doi: 10.1007/s00101-017-0359-4. Epub 2017 Sep 15. Anaesthesist. 2017. PMID: 28914327 English.
-
Enhanced hippocampal neurogenesis mediated by PGC-1α-activated OXPHOS after neonatal low-dose Propofol exposure.Front Aging Neurosci. 2022 Jul 27;14:925728. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2022.925728. eCollection 2022. Front Aging Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 35966788 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aimone J. B., Wiles J., Gage F. H. (2006) Potential role for adult neurogenesis in the encoding of time in new memories. Nature Neuroscience 9: 723–727. - PubMed
-
- Altman J., Bayer S. A. (1990) Migration and distribution of two populations of hippocampal granule cell precursors during the perinatal and postnatal periods. Journal of Comparative Neurology 301: 365–381. - PubMed
-
- Ben-Ari Y. (2002) Excitatory actions of gaba during development: The nature of the nurture. Nature Reviews. Neuroscience 3: 728–739. - PubMed
-
- Bickler P. E., Zhan X., Fahlman C. S. (2005) Isoflurane preconditions hippocampal neurons against oxygen-glucose deprivation: Role of intracellular Ca2+ and mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling. Anesthesiology 103: 532–539. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

