PLIP: fully automated protein-ligand interaction profiler
- PMID: 25873628
- PMCID: PMC4489249
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkv315
PLIP: fully automated protein-ligand interaction profiler
Abstract
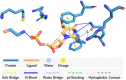
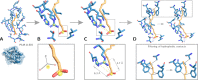
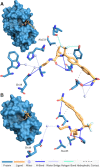
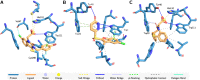
The characterization of interactions in protein-ligand complexes is essential for research in structural bioinformatics, drug discovery and biology. However, comprehensive tools are not freely available to the research community. Here, we present the protein-ligand interaction profiler (PLIP), a novel web service for fully automated detection and visualization of relevant non-covalent protein-ligand contacts in 3D structures, freely available at projects.biotec.tu-dresden.de/plip-web. The input is either a Protein Data Bank structure, a protein or ligand name, or a custom protein-ligand complex (e.g. from docking). In contrast to other tools, the rule-based PLIP algorithm does not require any structure preparation. It returns a list of detected interactions on single atom level, covering seven interaction types (hydrogen bonds, hydrophobic contacts, pi-stacking, pi-cation interactions, salt bridges, water bridges and halogen bonds). PLIP stands out by offering publication-ready images, PyMOL session files to generate custom images and parsable result files to facilitate successive data processing. The full python source code is available for download on the website. PLIP's command-line mode allows for high-throughput interaction profiling.
© The Author(s) 2015. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures

References
-
- Berman H.M. The Protein Data Bank: a historical perspective. Acta Crystallogr. A. 2008;64:88–95. - PubMed
-
- Desaphy J., Raimbaud E., Ducrot P., Rognan D. Encoding protein-ligand interaction patterns in fingerprints and graphs. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2013;53:623–637. - PubMed
-
- Liu Q., Kwoh C.K., Li J. Binding affinity prediction for protein-ligand complexes based on beta contacts and B factor. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2013;53:3076–3085. - PubMed
-
- Salentin S., Haupt V.J., Daminelli S., Schroeder M. Polypharmacology rescored: protein-ligand interaction profiles for remote binding site similarity assessment. Prog. Biophys. Mol. Biol. 2014;116:174–186. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

