Aspergillosis superinfection as a cause of death of crizotinib-induced interstitial lung disease successfully treated with high-dose corticosteroid therapy
- PMID: 25873886
- PMCID: PMC4395825
- DOI: 10.1159/000381209
Aspergillosis superinfection as a cause of death of crizotinib-induced interstitial lung disease successfully treated with high-dose corticosteroid therapy
Abstract
Crizotinib is an efficacious and well-tolerated drug in the management of ALK-positive lung cancer. Crizotinib treatment, however, is rarely complicated by the occurrence of acute interstitial lung disease (ILD) that is often fatal. There is no treatment for this serious adverse event. We report a female non-small cell lung cancer patient who developed ILD after a few days of crizotinib therapy. She showed a significant improvement after a high dose of pulse corticosteroid therapy, both radiologically and clinically. Unfortunately, the patient subsequently developed an aspergillosis superinfection leading to death. Our experience suggests that high-dose steroid therapy may be efficacious in the management of a severe complication of crizotinib therapy. However, potent antifungal therapy should be considered to prevent the risk of severe aspergillosis.
Keywords: Acute interstitial lung disease; Crizotinib; Non-small cell lung cancer.
Figures
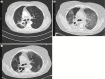
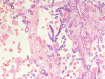
Similar articles
-
Acute interstitial lung disease in a patient with anaplastic lymphoma kinase-positive non-small-cell lung cancer after crizotinib therapy.Oxf Med Case Reports. 2014 Apr 8;2014(1):11-2. doi: 10.1093/omcr/omu004. eCollection 2014 Apr. Oxf Med Case Reports. 2014. PMID: 25988009 Free PMC article.
-
Interstitial Lung Disease Onset and Its Risk Factors in Japanese Patients With ALK-Positive NSCLC After Treatment With Crizotinib.J Thorac Oncol. 2019 Apr;14(4):672-682. doi: 10.1016/j.jtho.2018.11.022. Epub 2018 Dec 3. J Thorac Oncol. 2019. PMID: 30521972
-
Successful treatment with alectinib after crizotinib-induced interstitial lung disease.Lung Cancer. 2015 Dec;90(3):610-3. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2015.09.019. Epub 2015 Sep 25. Lung Cancer. 2015. PMID: 26452431
-
Management of crizotinib therapy for ALK-rearranged non-small cell lung carcinoma: an expert consensus.Lung Cancer. 2015 Feb;87(2):89-95. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2014.12.010. Epub 2014 Dec 18. Lung Cancer. 2015. PMID: 25576294 Review.
-
ALK inhibitors: what is the best way to treat patients with ALK+ non-small-cell lung cancer?Clin Lung Cancer. 2014 Sep;15(5):313-9. doi: 10.1016/j.cllc.2014.05.001. Epub 2014 Jun 2. Clin Lung Cancer. 2014. PMID: 24984564 Review.
Cited by
-
Second- and third-generation ALK inhibitors for non-small cell lung cancer.J Hematol Oncol. 2016 Mar 8;9:19. doi: 10.1186/s13045-016-0251-8. J Hematol Oncol. 2016. PMID: 26951079 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fungal Infections with Ibrutinib and Other Small-Molecule Kinase Inhibitors.Curr Fungal Infect Rep. 2019 Sep;13(3):86-98. doi: 10.1007/s12281-019-00343-9. Epub 2019 Jul 5. Curr Fungal Infect Rep. 2019. PMID: 31555394 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Shaw AT, Kim D-W, Nakagawa K, Seto T, Crinó L, et al. Crizotinib versus chemotherapy in advanced ALK-positive lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2013;368:2385–2394. - PubMed
-
- Roskoski R., Jr Anaplastic lymphoma kinase (ALK): structure, oncogenic activation, and pharmacological inhibition. Pharmacol Res. 2013;68:68–94. - PubMed
-
- Aparicio G, Calvo MB, Medina V, et al. Comprehensive lung injury pathology induced by mTOR inhibitors. Clin Transl Oncol. 2009;11:499–510. - PubMed
-
- Mukhopadhyay S, Parambil JG. Acute interstitial pneumonia (AIP): relationship to Hamman-Rich syndrome, diffuse alveolar damage (DAD), and acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) Semin Respir Crit Care Med. 2012;33:476–485. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

