A pretargeting system for tumor PET imaging and radioimmunotherapy
- PMID: 25873896
- PMCID: PMC4379897
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2015.00054
A pretargeting system for tumor PET imaging and radioimmunotherapy
Abstract
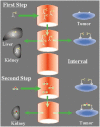
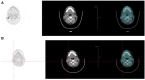
Labeled antibodies, as well as their fragments and antibody-derived recombinant constructs, have long been proposed as general vectors to target radionuclides to tumor lesions for imaging and therapy. They have indeed shown promise in both imaging and therapeutic applications, but they have not fulfilled the original expectations of achieving sufficient image contrast for tumor detection or sufficient radiation dose delivered to tumors for therapy. Pretargeting was originally developed for tumor immunoscintigraphy. It was assumed that directly-radiolabled antibodies could be replaced by an unlabeled immunoconjugate capable of binding both a tumor-specific antigen and a small molecular weight molecule. The small molecular weight molecule would carry the radioactive payload and would be injected after the bispecific immunoconjugate. It has been demonstrated that this approach does allow for both antibody-specific recognition and fast clearance of the radioactive molecule, thus resulting in improved tumor-to-normal tissue contrast ratios. It was subsequently shown that pretargeting also held promise for tumor therapy, translating improved tumor-to-normal tissue contrast ratios into more specific delivery of absorbed radiation doses. Many technical approaches have been proposed to implement pretargeting, and two have been extensively documented. One is based on the avidin-biotin system, and the other on bispecific antibodies binding a tumor-specific antigen and a hapten. Both have been studied in preclinical models, as well as in several clinical studies, and have shown improved targeting efficiency. This article reviews the historical and recent preclinical and clinical advances in the use of bispecific-antibody-based pretargeting for radioimmunodetection and radioimmunotherapy of cancer. The results of recent evaluation of pretargeting in PET imaging also are discussed.
Keywords: bispecific antibody; immuno-PET; immunoscintigraphy; pretargeting; radioimmunotherapy.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Pretargeted imaging and radioimmunotherapy of cancer using antibodies and bioorthogonal chemistry.Front Med (Lausanne). 2014 Nov 18;1:44. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2014.00044. eCollection 2014. Front Med (Lausanne). 2014. PMID: 25593917 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cancer Imaging and Therapy with Bispecific Antibody Pretargeting.Update Cancer Ther. 2007 Mar;2(1):19-31. doi: 10.1016/j.uct.2007.04.003. Update Cancer Ther. 2007. PMID: 18311322 Free PMC article.
-
Pretargeted radioimmunotherapy of cancer: progress step by step.J Nucl Med. 2003 Mar;44(3):400-11. J Nucl Med. 2003. PMID: 12621007 Review.
-
Tumor pretargeting for radioimmunodetection and radioimmunotherapy.J Nucl Med. 1998 Jan;39(1):65-76. J Nucl Med. 1998. PMID: 9443740
-
Avidin-biotin system pretargeting radioimmunoimaging and radioimmunotherapy and its application in mouse model of human colon carcinoma.World J Gastroenterol. 2005 Oct 28;11(40):6288-94. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v11.i40.6288. World J Gastroenterol. 2005. PMID: 16419157 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Sensitivity of pretargeted immunoPET using 68Ga-peptide to detect colonic carcinoma liver metastases in a murine xenograft model: Comparison with 18FDG PET-CT.Oncotarget. 2018 Jun 8;9(44):27502-27513. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.25514. eCollection 2018 Jun 8. Oncotarget. 2018. PMID: 29938001 Free PMC article.
-
Bispecific Antibodies: From Research to Clinical Application.Front Immunol. 2021 May 5;12:626616. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.626616. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34025638 Free PMC article.
-
Biotin-streptavidin-guided two-step pretargeting approach using PLGA for molecular ultrasound imaging and chemotherapy for ovarian cancer.PeerJ. 2021 May 25;9:e11486. doi: 10.7717/peerj.11486. eCollection 2021. PeerJ. 2021. PMID: 34113492 Free PMC article.
-
Bioorthogonal two-component drug delivery in HER2(+) breast cancer mouse models.Sci Rep. 2016 Apr 12;6:24298. doi: 10.1038/srep24298. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27068794 Free PMC article.
-
Anti-tax interacting protein-1 (TIP-1) monoclonal antibody targets human cancers.Oncotarget. 2016 Jul 12;7(28):43352-43362. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.9713. Oncotarget. 2016. PMID: 27270318 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Barbet J., Peltier P., Bardet S., Vuillez J. P., Bachelot I., Denet S., et al. . (1998). Radioimmunodetection of medullary thyroid carcinoma using indium-111 bivalent hapten and anti-CEA x anti-DTPA-indium bispecific antibody. J. Nucl. Med. 39, 1172–1178. - PubMed
-
- Boerman O. C., Kranenborg M. H., Oosterwijk E., Griffiths G. L., McBride W. J., Oyen W. J., et al. . (1999). Pretargeting of renal cell carcinoma: improved tumor targeting with a bivalent chelate. Cancer Res. 59, 4400–4405. - PubMed
-
- Bos E. S., Kuijpers W. H., Meesters-Winters M., Pham D. T., de Haan A. S., van Doornmalen A. M., et al. . (1994). In vitro evaluation of DNA-DNA hybridization as a two-step approach in radioimmunotherapy of cancer. Cancer Res. 54, 3479–3486. - PubMed
-
- Chang C. H., Sharkey R. M., Rossi E. A., Karacay H., McBride W., Hansen H. J., et al. . (2002). Molecular advances in pretargeting radioimunotherapy with bispecific antibodies. Mol. Cancer Ther. 1, 553–563. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

