The effect of low-frequency road noise on driver sleepiness and performance
- PMID: 25874883
- PMCID: PMC4398381
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0123835
The effect of low-frequency road noise on driver sleepiness and performance
Abstract
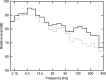
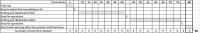
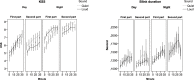
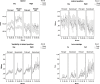
It is a well-known fact today that driver sleepiness is a contributory factor in crashes. Factors considered as sleepiness contributor are mostly related to time of the day, hours being awake and hours slept. Factors contributing to active and passive fatigue are mostly focusing on the level of cognitive load. Less is known what role external factors, e.g. type of road, sound/noise, vibrations etc., have on the ability to stay awake both under conditions of sleepiness and under active or passive fatigue. The aim of this moving base driving simulator study with 19 drivers participating in a random order day and night time, was to evaluate the effect of low-frequency road noise on driver sleepiness and performance, including both long-term and short-term effects. The results support to some extent the hypothesis that road-induced interior vehicle sound affects driving performance and driver sleepiness. Increased low-frequency noise helps to reduce speed during both day- and night time driving, but also contributes to increase the number of lane crossings during night time.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Horne J, Reyner L. Driver sleepiness. J Sleep Res 1995;4: 23–29. - PubMed
-
- Stutts J, Wilkins J, Scott O, Vaughn B. Driver risk factors for sleep-related crashes. Accid Anal Prev 2003;35: 321–331. - PubMed
-
- Åkerstedt T, Kecklund G. Age, gender and early morning highway accidents. J Sleep Res 2001;10: 105–110. - PubMed
-
- Wake up to the risks of drowsy driving. Consumer reports 2004; 69: 23 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

