Ex vivo cytosolic delivery of functional macromolecules to immune cells
- PMID: 25875117
- PMCID: PMC4395260
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0118803
Ex vivo cytosolic delivery of functional macromolecules to immune cells
Abstract
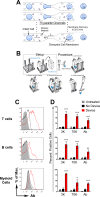
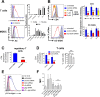
Intracellular delivery of biomolecules, such as proteins and siRNAs, into primary immune cells, especially resting lymphocytes, is a challenge. Here we describe the design and testing of microfluidic intracellular delivery systems that cause temporary membrane disruption by rapid mechanical deformation of human and mouse immune cells. Dextran, antibody and siRNA delivery performance is measured in multiple immune cell types and the approach's potential to engineer cell function is demonstrated in HIV infection studies.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Kalos M, Levine BL, Porter DL, Katz S, Grupp SA, Bagg A, et al. T cells with chimeric antigen receptors have potent antitumor effects and can establish memory in patients with advanced leukemia. Science translational medicine. 2011;3(95):95ra73–95ra73. 10.1126/scitranslmed.3002842 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Small EJ, Schellhammer PF, Higano CS, Redfern CH, Nemunaitis JJ, Valone FH, et al. Placebo-controlled phase III trial of immunologic therapy with sipuleucel-T (APC8015) in patients with metastatic, asymptomatic hormone refractory prostate cancer. Journal of Clinical Oncology. 2006;24(19):3089–94. - PubMed
-
- Zorko M, Langel Ü. Cell-penetrating peptides: mechanism and kinetics of cargo delivery. Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews. 2005;57(4):529–45. - PubMed
-
- Song E, Zhu P, Lee S-K, Chowdhury D, Kussman S, Dykxhoorn DM, et al. Antibody mediated in vivo delivery of small interfering RNAs via cell-surface receptors. Nature biotechnology. 2005;23(6):709–17. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

