Association between the European GWAS-identified susceptibility locus at chromosome 4p16 and the risk of atrial septal defect: a case-control study in Southwest China and a meta-analysis
- PMID: 25875170
- PMCID: PMC4395394
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0123959
Association between the European GWAS-identified susceptibility locus at chromosome 4p16 and the risk of atrial septal defect: a case-control study in Southwest China and a meta-analysis
Abstract
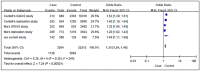
Atrial septal defect (ASD) is the third most frequent type of congenital heart anomaly, featuring shunting of blood between the two atria. Gene-environment interaction remains to be an acknowledged cause for ASD occurrence. A recent European genome-wide association study (GWAS) of congenital heart disease (CHD) identified 3 susceptibility SNPs at chromosome 4p16 associated with ASD: rs870142, rs16835979 and rs6824295. A Chinese-GWAS of CHD conducted in the corresponding period did not reveal the 3 susceptibility SNPs, but reported 2 different risk SNPs: rs2474937 and rs1531070. Therefore, we aimed to investigate the associations between the 3 European GWAS-identified susceptibility SNPs and ASD risk in the Han population in southwest China. Additionally, to increase the robustness of our current analysis, we conducted a meta-analysis combining published studies and our current case-control study. We performed association, linkage disequilibrium, and haplotype analysis among the 3 SNPs in 190 ASD cases and 225 age-, sex-, and ethnicity-matched healthy controls. Genotype and allele frequencies among the 3 SNPs showed statistically significant differences between the cases and controls. Our study found that individuals carrying the allele T of rs870142, the allele A of rs16835979, and the allele T of rs6824295 had a respective 50.1% (odds ratio (OR) = 1.501, 95% confidence interval (CI) = 1.122-2.009, PFDR-BH = 0.018), 48.5% (OR = 1.485, 95%CI = 1.109-1.987, PFDR-BH = 0.012), and 38.6% (OR = 1.386, 95%CI = 1.042-1.844, PFDR-BH = 0.025) increased risk to develop ASD than wild-type allele carriers in our study cohort. In the haplotype analysis, we identified a disease-risk haplotype (TAT) (OR = 1.540, 95%CI = 1.030-2.380, PFDR-BH = 0.016). Our meta-analysis also showed that the investigated SNP was associated with ASD risk (combined OR (95%CI) = 1.35 (1.24-1.46), P < 0.00001). Our study provides compelling evidence to motivate better understanding of the etiology of ASD.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Replication of the 4p16 susceptibility locus in congenital heart disease in Han Chinese populations.PLoS One. 2014 Sep 12;9(9):e107411. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0107411. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25215500 Free PMC article.
-
Association Between the 4p16 Susceptibility Locus and the Risk of Atrial Septal Defect in Population from Southeast China.Pediatr Cardiol. 2016 Jan;37(1):120-4. doi: 10.1007/s00246-015-1248-8. Epub 2015 Aug 19. Pediatr Cardiol. 2016. PMID: 26283177
-
Genome-wide association study of multiple congenital heart disease phenotypes identifies a susceptibility locus for atrial septal defect at chromosome 4p16.Nat Genet. 2013 Jul;45(7):822-4. doi: 10.1038/ng.2637. Epub 2013 May 26. Nat Genet. 2013. PMID: 23708191 Free PMC article.
-
Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of SNPs from Genome-Wide Association Studies of Head and Neck Cancer.Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2018 Oct;159(4):615-624. doi: 10.1177/0194599818792262. Epub 2018 Aug 21. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2018. PMID: 30126334
-
Critical Analysis of Genome-Wide Association Studies: Triple Negative Breast Cancer Quae Exempli Causa.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Aug 14;21(16):5835. doi: 10.3390/ijms21165835. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32823908 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Phenotype of ASDs Associated With 4p16 Risk Locus and Novel Genome-Wide Associations of ASD Patients in the Finnish Population.Circ Genom Precis Med. 2023 Oct;16(5):486-489. doi: 10.1161/CIRCGEN.123.004070. Epub 2023 Aug 14. Circ Genom Precis Med. 2023. PMID: 37577800 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Congenital heart disease risk loci identified by genome-wide association study in European patients.J Clin Invest. 2021 Jan 19;131(2):e141837. doi: 10.1172/JCI141837. J Clin Invest. 2021. PMID: 33201861 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Human Genetics of Atrial Septal Defect.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2024;1441:467-480. doi: 10.1007/978-3-031-44087-8_24. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2024. PMID: 38884726 Review.
-
A novel RNA-mediated mechanism causing down-regulation of insulating promoter interactions in human embryonic stem cells.Sci Rep. 2021 Dec 1;11(1):23233. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-02373-1. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34853328 Free PMC article.
-
A genome-wide association study of obstructive heart defects among participants in the National Birth Defects Prevention Study.Am J Med Genet A. 2022 Aug;188(8):2303-2314. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.a.62759. Epub 2022 Apr 22. Am J Med Genet A. 2022. PMID: 35451555 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources