Mining disease risk patterns from nationwide clinical databases for the assessment of early rheumatoid arthritis risk
- PMID: 25875441
- PMCID: PMC4395408
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0122508
Mining disease risk patterns from nationwide clinical databases for the assessment of early rheumatoid arthritis risk
Abstract
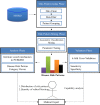
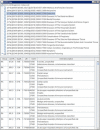
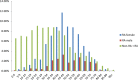
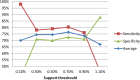
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a chronic autoimmune rheumatic disease that can cause painful swelling in the joint lining, morning stiffness, and joint deformation/destruction. These symptoms decrease both quality of life and life expectancy. However, if RA can be diagnosed in the early stages, it can be controlled with pharmacotherapy. Although many studies have examined the possibility of early assessment and diagnosis, few have considered the relationship between significant risk factors and the early assessment of RA. In this paper, we present a novel framework for early RA assessment that utilizes data preprocessing, risk pattern mining, validation, and analysis. Under our proposed framework, two risk patterns can be discovered. Type I refers to well-known risk patterns that have been identified by existing studies, whereas Type II denotes unknown relationship risk patterns that have rarely or never been reported in the literature. These Type II patterns are very valuable in supporting novel hypotheses in clinical trials of RA, and constitute the main contribution of this work. To ensure the robustness of our experimental evaluation, we use a nationwide clinical database containing information on 1,314 RA-diagnosed patients over a 12-year follow-up period (1997-2008) and 965,279 non-RA patients. Our proposed framework is employed on this large-scale population-based dataset, and is shown to effectively discover rich RA risk patterns. These patterns may assist physicians in patient assessment, and enhance opportunities for early detection of RA. The proposed framework is broadly applicable to the mining of risk patterns for major disease assessments. This enables the identification of early risk patterns that are significantly associated with a target disease.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
eDRAM: Effective early disease risk assessment with matrix factorization on a large-scale medical database: A case study on rheumatoid arthritis.PLoS One. 2018 Nov 26;13(11):e0207579. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0207579. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 30475847 Free PMC article.
-
Mining Sequential Risk Patterns From Large-Scale Clinical Databases for Early Assessment of Chronic Diseases: A Case Study on Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease.IEEE J Biomed Health Inform. 2017 Mar;21(2):303-311. doi: 10.1109/JBHI.2017.2657802. Epub 2017 Jan 25. IEEE J Biomed Health Inform. 2017. PMID: 28129195
-
Databases of patients with early rheumatoid arthritis in the USA.Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2003 Sep-Oct;21(5 Suppl 31):S146-53. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2003. PMID: 14969067 Review.
-
[Detecting shared pathways linked to rheumatoid arthritis with other autoimmune diseases in a in silico analysis].Mol Biol (Mosk). 2016 May-Jun;50(3):530-9. doi: 10.7868/S0026898416030149. Mol Biol (Mosk). 2016. PMID: 27414792 Russian.
-
Uniform databases in early arthritis: specific measures to complement classification criteria and indices of clinical change.Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2003 Sep-Oct;21(5 Suppl 31):S79-88. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2003. PMID: 14969056 Review.
Cited by
-
Patient Stratification Using Electronic Health Records from a Chronic Disease Management Program.IEEE J Biomed Health Inform. 2016 Jan 4:10.1109/JBHI.2016.2514264. doi: 10.1109/JBHI.2016.2514264. Online ahead of print. IEEE J Biomed Health Inform. 2016. PMID: 26742152 Free PMC article.
-
The index lift in data mining has a close relationship with the association measure relative risk in epidemiological studies.BMC Med Inform Decis Mak. 2019 Jun 17;19(1):112. doi: 10.1186/s12911-019-0838-4. BMC Med Inform Decis Mak. 2019. PMID: 31208407 Free PMC article.
-
Big data analytics for preventive medicine.Neural Comput Appl. 2020;32(9):4417-4451. doi: 10.1007/s00521-019-04095-y. Epub 2019 Mar 16. Neural Comput Appl. 2020. PMID: 32205918 Free PMC article.
-
eDRAM: Effective early disease risk assessment with matrix factorization on a large-scale medical database: A case study on rheumatoid arthritis.PLoS One. 2018 Nov 26;13(11):e0207579. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0207579. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 30475847 Free PMC article.
-
TriSpectraKAN: a novel approach for COPD detection via lung sound analysis.Sci Rep. 2025 Feb 21;15(1):6296. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-82781-1. Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 39984500 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gibofsky A. Overview of epidemiology, pathophysiology, and diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis. The American Journal of Managed Care. 2012. Dec;18(13 Suppl):S295–302. - PubMed
-
- Mathias JS, Agrawal A, Feinglass J, Cooper AJ, Baker DW, Choudhary A. Development of a 5 year life expectancy index in older adults using predictive mining of electronic health record data. Journal of the American Medical Informatics Association. 2013. Jun;20(e1):e118–e24. 10.1136/amiajnl-2012-001360 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

