The Brainstem Oscillator for Whisking and the Case for Breathing as the Master Clock for Orofacial Motor Actions
- PMID: 25876629
- PMCID: PMC4924579
- DOI: 10.1101/sqb.2014.79.024794
The Brainstem Oscillator for Whisking and the Case for Breathing as the Master Clock for Orofacial Motor Actions
Abstract
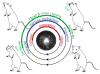
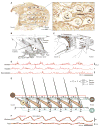
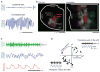
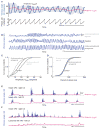
Whisking and sniffing are predominant aspects of exploratory behavior in rodents. We review evidence that these motor rhythms are coordinated by the respiratory patterning circuitry in the ventral medulla. A recently described region in the intermediate reticular zone of the medulla functions as an autonomous whisking oscillator, whose neuronal output is reset upon each breath by input from the pre-Bötzinger complex. Based on similarities between this neuronal circuit architecture and that of other orofacial behaviors, we propose that the pre-Bötzinger complex, which projects broadly to premotor regions throughout the intermediate reticular zone of the medulla, functions as a master clock to coordinate multiple orofacial actions involved in exploratory and ingestive behaviors. We then extend the analysis of whisking to the relatively slow control of the midpoint of the whisk. We conjecture, in a manner consistent with breathing as the "master clock" for all orofacial behaviors, that slow control optimizes the position of sensors whereas the breathing rhythm provides a means to perceptually bind the inputs from different orofacial modalities.
Copyright © 2014 Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press; all rights reserved.
Figures



References
-
- Berg RW, Kleinfeld D. Rhythmic whisking by rat: Retraction as well as protraction of the vibrissae is under active muscular control. Journal of Neurophysiology. 2003;89:104–117. - PubMed
-
- Bieger D, Hopkins DA. Viscerotopic representation of the upper alimentary tract in the medulla oblongata in the rat: The nucleus ambiguus. Journal of Comparative Neurology. 1987;262:546–562. - PubMed
-
- Bouvier J, Thoby-Brisson M, NR, Dubreuil V, Ericson J, Champagnat J, Pierani A, AC, Fortin G. Hindbrain interneurons and axon guidance signaling critical for breathing. Nature Neuroscience. 2010;13:1066–1074. - PubMed
-
- Brecht M, Krauss A, Muhammad S, Sinai-Esfahani L, Bellanca S, Margrie TW. Organization of rat vibrissa motor cortex and adjacent areas according to cytoarchitectonics, microstimulation, and intracellular stimulation of identified cells. Jounal of Comparative Neurology. 2004;479:360–373. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
