The Role of Phosphorylated Cx43 on PKC Mediated Ser368 in Lung Injury Induced by Seawater Inhalation
- PMID: 25876711
- PMCID: PMC4560767
- DOI: 10.1007/s10753-015-0162-9
The Role of Phosphorylated Cx43 on PKC Mediated Ser368 in Lung Injury Induced by Seawater Inhalation
Abstract
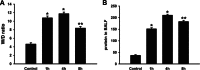
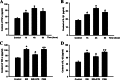
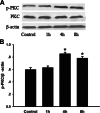
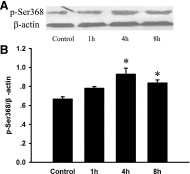
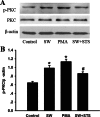
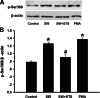
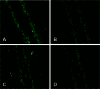
Seawater aspiration may result in acute lung injury/acute respiratory distress syndrome (ALI/ARDS), which is characterized by pulmonary inflammation and lung edema that closely related to pulmonary barrier dysfunction and intracellular communication. The aim of the present research was to explore the role of connexion 43 (Cx43) in seawater aspiration-induced ALI/ARDS. The results from in vivo experiments showed that seawater inhalation led to increased expression of p-PKC and phosphorylated Cx43 (p-Cx43), which were followed by protein rich fluid leakage and TNF-α and IL-1β secretion. Besides, the results from in vitro tests proved that the expression of p-PKC directly influenced phosphorylation state of Cx43 and its function, which could further affect the inflammatory factors secretion and intercellular communication. In conclusion, seawater aspiration causes p-Cx43 expression by PKC pathway, which is involved in the on come and development of pulmonary inflammation and lung edema.
Figures
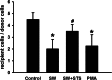
Similar articles
-
3,5,4'-tri-O-acetylresveratrol ameliorates seawater exposure-induced lung injury by upregulating connexin 43 expression in lung.Mediators Inflamm. 2013;2013:182132. doi: 10.1155/2013/182132. Epub 2013 Mar 12. Mediators Inflamm. 2013. PMID: 23576849 Free PMC article.
-
3,5,4'-Tri-O-acetylresveratrol attenuates seawater inhalation-induced acute respiratory distress syndrome via thioredoxin 1 pathway.Int J Mol Med. 2018 Jun;41(6):3493-3500. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2018.3528. Epub 2018 Mar 1. Int J Mol Med. 2018. PMID: 29512754
-
Participation of autophagy in acute lung injury induced by seawater.Exp Lung Res. 2013 Dec;39(10):441-52. doi: 10.3109/01902148.2013.845626. Epub 2013 Nov 18. Exp Lung Res. 2013. PMID: 24245991
-
Protein kinase C and acute respiratory distress syndrome.Shock. 2013 Jun;39(6):467-79. doi: 10.1097/SHK.0b013e318294f85a. Shock. 2013. PMID: 23572089 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of Connexin 43 in Lung Disease.Life (Basel). 2020 Dec 19;10(12):363. doi: 10.3390/life10120363. Life (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33352732 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Lung injury after asphyxia and hemorrhagic shock in newborn piglets: Analysis of structural and inflammatory changes.PLoS One. 2019 Jul 5;14(7):e0219211. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0219211. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 31276543 Free PMC article.
-
Seawater-drowning-induced acute lung injury: From molecular mechanisms to potential treatments.Exp Ther Med. 2017 Jun;13(6):2591-2598. doi: 10.3892/etm.2017.4302. Epub 2017 Apr 5. Exp Ther Med. 2017. PMID: 28587319 Free PMC article.
-
Hypoxia‑induced internalization of connexin 26 and connexin 43 in pulmonary epithelial cells is involved in the occurrence of non‑small cell lung cancer via the P53/MDM2 signaling pathway.Int J Oncol. 2019 Oct;55(4):845-859. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2019.4867. Epub 2019 Sep 3. Int J Oncol. 2019. PMID: 31485592 Free PMC article.
-
Carbon Monoxide Attenuates Lipopolysaccharides (LPS)-Induced Acute Lung Injury in Neonatal Rats via Downregulation of Cx43 to Reduce Necroptosis.Med Sci Monit. 2019 Aug 20;25:6255-6263. doi: 10.12659/MSM.917751. Med Sci Monit. 2019. PMID: 31429423 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

