A review of the effects of FSCV and microdialysis measurements on dopamine release in the surrounding tissue
- PMID: 25876757
- PMCID: PMC4437820
- DOI: 10.1039/c4an02065k
A review of the effects of FSCV and microdialysis measurements on dopamine release in the surrounding tissue
Abstract
Microdialysis is commonly used in neuroscience to obtain information about the concentration of substances, including neurotransmitters such as dopamine (DA), in the extracellular space (ECS) of the brain. Measuring DA concentrations in the ECS with in vivo microdialysis and/or voltammetry is a mainstay of investigations into both normal and pathological function of central DA systems. Although both techniques are instrumental in understanding brain chemistry each has its shortcomings. The objective of this review is to characterize some of the tissue and DA differences associated with each technique in vivo. Much of this work will focus on immunohistochemical and microelectrode measurements of DA in the tissue next to the microdialysis probe and mitigating the response to the damage caused by probe implantation.
Figures






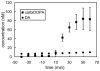

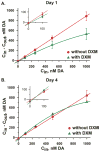


Similar articles
-
Microdialysis of dopamine interpreted with quantitative model incorporating probe implantation trauma.J Neurochem. 2003 Aug;86(4):932-46. doi: 10.1046/j.1471-4159.2003.01904.x. J Neurochem. 2003. PMID: 12887691 Free PMC article.
-
A novel electrochemical approach for prolonged measurement of absolute levels of extracellular dopamine in brain slices.ACS Chem Neurosci. 2015 Nov 18;6(11):1802-12. doi: 10.1021/acschemneuro.5b00120. Epub 2015 Sep 10. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 26322962
-
Direct comparison of the response of voltammetry and microdialysis to electrically evoked release of striatal dopamine.J Neurochem. 1998 Feb;70(2):584-93. doi: 10.1046/j.1471-4159.1998.70020584.x. J Neurochem. 1998. PMID: 9453552
-
Microdialysis applications in neuroscience.Neurol Res. 2008 Sep;30(7):661-8. doi: 10.1179/174313208X289570. Epub 2008 Jul 15. Neurol Res. 2008. PMID: 18631429 Review.
-
In vivo monitoring of brain neurotransmitter release for the assessment of neuroendocrine interactions.Cell Mol Neurobiol. 1996 Jun;16(3):383-96. doi: 10.1007/BF02088102. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 1996. PMID: 8818403 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Measuring tryptophan dynamics using fast scan cyclic voltammetry at carbon fiber microelectrodes with improved sensitivity and selectivity.RSC Adv. 2023 Sep 4;13(37):26203-26212. doi: 10.1039/d3ra04551j. eCollection 2023 Aug 29. RSC Adv. 2023. PMID: 37671005 Free PMC article.
-
Multiplexing FSCV and iGluSnFR3 Sensors Reveals Adenosine Transiently Inhibits Stimulated Dopamine and Glutamate Release.J Neurochem. 2025 Jul;169(7):e70147. doi: 10.1111/jnc.70147. J Neurochem. 2025. PMID: 40621619 Free PMC article.
-
Thin layer cell behavior of CNT yarn and cavity carbon nanopipette electrodes: Effect on catecholamine detection.Electrochim Acta. 2020 Nov 20;361:137032. doi: 10.1016/j.electacta.2020.137032. Epub 2020 Sep 5. Electrochim Acta. 2020. PMID: 32981947 Free PMC article.
-
A chemogenetic approach for dopamine imaging with tunable sensitivity.Nat Commun. 2024 Jul 2;15(1):5551. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-49442-3. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 38956067 Free PMC article.
-
Frontiers in Electrochemical Sensors for Neurotransmitter Detection: Towards Measuring Neurotransmitters as Chemical Diagnostics for Brain Disorders.Anal Methods. 2019 Jun 6;11(21):2738-2755. doi: 10.1039/c9ay00055k. Epub 2019 May 16. Anal Methods. 2019. PMID: 32724337 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Arbuthnott GW, Fairbrother IS, Butcher SP. J Neurosci Methods. 1990;34:73–81. - PubMed
-
- Bosche B, Dohmen C, Graf R, Neveling M, Staub F, Kracht L, Sobesky J, Lehnhardt FG, Heiss WD. Stroke. 2003;34:2908–2913. - PubMed
-
- Di Chiara G. J Psychopharmacol. 1998;12:54–67. - PubMed
-
- Kehr J. In: Handbook of Behavioral Neuroscience. Ben HCW, Thomas IFHC, editors. Vol. 16. Elsevier; 2006. pp. 111–129.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

