A RASopathy gene commonly mutated in cancer: the neurofibromatosis type 1 tumour suppressor
- PMID: 25877329
- PMCID: PMC4822336
- DOI: 10.1038/nrc3911
A RASopathy gene commonly mutated in cancer: the neurofibromatosis type 1 tumour suppressor
Abstract
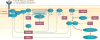
Neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1) is a common genetic disorder that predisposes affected individuals to tumours. The NF1 gene encodes a RAS GTPase-activating protein called neurofibromin and is one of several genes that (when mutant) affect RAS-MAPK signalling, causing related diseases collectively known as RASopathies. Several RASopathies, beyond NF1, are cancer predisposition syndromes. Somatic NF1 mutations also occur in 5-10% of human sporadic cancers and may contribute to resistance to therapy. To highlight areas for investigation in RASopathies and sporadic tumours with NF1 mutations, we summarize current knowledge of NF1 disease, the NF1 gene and neurofibromin, neurofibromin signalling pathways and recent developments in NF1 therapeutics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- Crowe FW, Schull WJ, Neel JV. A Clinical, Pathological and Genetic Study of Multiple Neurofibromatosis. Charles C. Thomas; 1956.
-
- Evans DG, et al. Birth incidence and prevalence of tumor-prone syndromes: estimates from a UK family genetic register service. Am J Med Genet A. 2010;152A:327–332. - PubMed
-
- Friedman JM, Birch PH. Type 1 neurofibromatosis: a descriptive analysis of the disorder in 1,728 patients. Am J Med Genet. 1997;70:138–143. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

