Contamination of sulfonamide antibiotics and sulfamethazine-resistant bacteria in the downstream and estuarine areas of Jiulong River in Southeast China
- PMID: 25877900
- PMCID: PMC4515247
- DOI: 10.1007/s11356-015-4473-z
Contamination of sulfonamide antibiotics and sulfamethazine-resistant bacteria in the downstream and estuarine areas of Jiulong River in Southeast China
Abstract
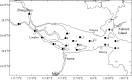
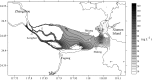
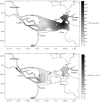
Surface water samples from downstream and estuarine areas of Jiulong River were collected in August 2011 and May 2012 for detecting sulfonamide antibiotic residues and isolating sulfamethazine-resistant bacteria. Sulfamethazine was detected in all samples in May 2012 at an average concentration of 78.3 ng L(-1), which was the highest among the nine sulfonamide antibiotics determined. Sulfamethazine-resistant bacteria (SRB) were screened using antibiotic-containing agar plates. The SRB average abundance in the samples was 3.69 × 10(4) and 2.17 × 10(3) CFUs mL(-1) in August 2011 and May 2012, respectively, and was positively correlated to sulfamethazine concentration in May 2012. The 16S rRNA gene sequencing of all the 121 SRB isolates revealed high diversity. Furthermore, the SRB isolates exhibited multidrug resistance, with 48.7% showing resistance to at least three antibiotics. The abundance and persistence of highly diverse SRB and their multidrug resistance are likely to demonstrate the transferable pressure from coastal environments on public health.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Antibiotics pollution in Jiulong River estuary: source, distribution and bacterial resistance.Chemosphere. 2011 Sep;84(11):1677-85. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2011.04.076. Epub 2011 May 26. Chemosphere. 2011. PMID: 21620433
-
Occurrence of antibiotics and antibiotic resistance genes in a sewage treatment plant and its effluent-receiving river.Chemosphere. 2015 Jan;119:1379-1385. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2014.02.040. Epub 2014 Mar 12. Chemosphere. 2015. PMID: 24630248
-
Spatiotemporal profile of tetracycline and sulfonamide and their resistance on a catchment scale.Environ Pollut. 2018 Oct;241:1098-1105. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2018.06.050. Epub 2018 Jun 19. Environ Pollut. 2018. PMID: 30029318
-
[Novel molecular mechanisms of antibiotic resistance found in clinically isolated pathogenic bacteria].Nihon Saikingaku Zasshi. 2009 Dec;64(2-4):357-64. doi: 10.3412/jsb.64.357. Nihon Saikingaku Zasshi. 2009. PMID: 19721338 Review. Japanese. No abstract available.
-
Bacteria That Make a Meal of Sulfonamide Antibiotics: Blind Spots and Emerging Opportunities.Environ Sci Technol. 2018 Apr 3;52(7):3854-3868. doi: 10.1021/acs.est.7b06026. Epub 2018 Mar 13. Environ Sci Technol. 2018. PMID: 29498514 Review.
Cited by
-
Antibiotic resistance genes in China: occurrence, risk, and correlation among different parameters.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2018 Aug;25(22):21467-21482. doi: 10.1007/s11356-018-2507-z. Epub 2018 Jun 12. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2018. PMID: 29948704 Review.
-
Simultaneous determination of sulfonamides and fluoroquinolones from environmental water based on magnetic double-template molecularly imprinting technique.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2018 Jun;25(16):16121-16134. doi: 10.1007/s11356-018-1581-6. Epub 2018 Mar 29. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2018. PMID: 29594906
-
Comparison of disinfection by-products formed by preoxidation of sulfamethazine by K2FeO4 and O3 and the influence on cytotoxicity and biological toxicity.Front Chem. 2022 Aug 19;10:904867. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2022.904867. eCollection 2022. Front Chem. 2022. PMID: 36059877 Free PMC article.
-
Density functional theory study of direct and indirect photodegradation mechanisms of sulfameter.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2016 Oct;23(19):19921-30. doi: 10.1007/s11356-016-6956-y. Epub 2016 Jul 16. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2016. PMID: 27424205
-
Selective determination of sulfonamides from environmental water based on magnetic surface molecularly imprinting technology.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2017 Apr;24(10):9174-9186. doi: 10.1007/s11356-017-8581-9. Epub 2017 Feb 18. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2017. PMID: 28214939
References
-
- Biyela PT, Lin J, Bezuidenhout CC, Morris R. The role of aquatic ecosystems as reservoirs of antibiotic resistant bacteria and antibiotic resistance genes. London: IWA Publishing; 2004. pp. 45–50. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

