Outcomes and costs of incorporating a multibiomarker disease activity test in the management of patients with rheumatoid arthritis
- PMID: 25877911
- PMCID: PMC4536857
- DOI: 10.1093/rheumatology/kev023
Outcomes and costs of incorporating a multibiomarker disease activity test in the management of patients with rheumatoid arthritis
Abstract
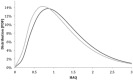
Objective: The multibiomarker disease activity (MBDA) blood test has been clinically validated as a measure of disease activity in patients with RA. We aimed to estimate the effect of the MBDA test on physical function for patients with RA (based on HAQ), quality-adjusted life years and costs over 10 years.
Methods: A decision analysis was conducted to quantify the effect of using the MBDA test on RA-related outcomes and costs to private payers and employers. Results of a clinical management study reporting changes to anti-rheumatic drug recommendations after use of the MBDA test informed clinical utility. The effect of treatment changes on HAQ was derived from 5 tight-control and 13 treatment-switch trials. Baseline HAQ scores and the HAQ score relationship with medical costs and quality of life were derived from published National Data Bank for Rheumatic Diseases data.
Results: Use of the MBDA test is projected to improve HAQ scores by 0.09 units in year 1, declining to 0.02 units after 10 years. Over the 10 year time horizon, quality-adjusted life years increased by 0.08 years and costs decreased by US$457 (cost savings in disability-related medical costs, US$659; in productivity costs, US$2137). The most influential variable in the analysis was the effect of the MBDA test on clinician treatment recommendations and subsequent HAQ changes.
Conclusion: The MBDA test aids in the assessment of disease activity in patients with RA by changing treatment decisions, improving the functional status of patients and cost savings. Further validation is ongoing and future longitudinal studies are warranted.
Keywords: biomarkers; health economics; outcome assessment; quality of life; rheumatoid arthritis.
© The Author 2015. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the British Society for Rheumatology.
Figures


Similar articles
-
A multibiomarker disease activity score for rheumatoid arthritis predicts radiographic joint damage in the BeSt study.J Rheumatol. 2014 Nov;41(11):2114-9. doi: 10.3899/jrheum.131412. Epub 2014 Aug 15. J Rheumatol. 2014. PMID: 25128518 Clinical Trial.
-
Cost-effective Tapering Algorithm in Patients with Rheumatoid Arthritis: Combination of Multibiomarker Disease Activity Score and Autoantibody Status.J Rheumatol. 2019 May;46(5):460-466. doi: 10.3899/jrheum.180028. Epub 2018 Dec 1. J Rheumatol. 2019. PMID: 30504510 Clinical Trial.
-
Costs in Relation to Disability, Disease Activity, and Health-related Quality of Life in Rheumatoid Arthritis: Observational Data from Southern Sweden.J Rheumatol. 2016 Jul;43(7):1292-9. doi: 10.3899/jrheum.150617. Epub 2016 Jun 1. J Rheumatol. 2016. PMID: 27252420
-
The economics of treatment in early rheumatoid arthritis.Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 2009 Feb;23(1):83-92. doi: 10.1016/j.berh.2008.11.005. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 2009. PMID: 19233048 Review.
-
The potential impact of monitoring disease activity biomarkers on rheumatoid arthritis outcomes and costs.Per Med. 2018 Jul 1;15(4):291-301. doi: 10.2217/pme-2018-0001. Epub 2018 Apr 25. Per Med. 2018. PMID: 29693487 Review.
Cited by
-
Reliable and cost-effective serodiagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis.Rheumatol Int. 2016 Jun;36(6):751-8. doi: 10.1007/s00296-016-3433-3. Epub 2016 Feb 9. Rheumatol Int. 2016. PMID: 26856871 Review.
-
Methodological aspects of design, analysis and reporting of studies with work participation as an outcome domain in patients with inflammatory arthritis: results of two systematic literature reviews informing EULAR points to consider.RMD Open. 2021 Feb;7(1):e001522. doi: 10.1136/rmdopen-2020-001522. RMD Open. 2021. PMID: 33542048 Free PMC article.
-
Review of biomarkers in systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis: helpful tools or just playing tricks?Arthritis Res Ther. 2016 Jul 13;18:163. doi: 10.1186/s13075-016-1069-z. Arthritis Res Ther. 2016. PMID: 27411444 Free PMC article.
-
Correlation of the Multi-Biomarker Disease Activity Score With Rheumatoid Arthritis Disease Activity Measures: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2019 Nov;71(11):1459-1472. doi: 10.1002/acr.23785. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2019. PMID: 30320973 Free PMC article.
-
Uptake and Clinical Utility of Multibiomarker Disease Activity Testing in the United States.J Rheumatol. 2019 Mar;46(3):237-244. doi: 10.3899/jrheum.180071. Epub 2018 Nov 15. J Rheumatol. 2019. PMID: 30442830 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alamanos Y, Voulgari PV, Drosos AA. Incidence and prevalence of rheumatoid arthritis, based on the 1987 American College of Rheumatology criteria: a systematic review. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2006;36:182–8. - PubMed
-
- Wasserman AM. Diagnosis and management of rheumatoid arthritis. Am Fam Physician. 2011;84: 1245–52. - PubMed
-
- Michaud K, Vera-Llonch M, Oster G. Mortality risk by functional status and health-related quality of life in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol. 2012;39:54–9. - PubMed
-
- Plant MJ, Williams AL, O’Sullivan MM, et al. Relationship between time-integrated C-reactive protein levels and radiologic progression in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2000;43:1473–7. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

