Efficacy of Methylphenidate Hydrochloride Extended-Release Capsules (Aptensio XR™) in Children and Adolescents with Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder: A Phase III, Randomized, Double-Blind Study
- PMID: 25877989
- PMCID: PMC4425805
- DOI: 10.1007/s40263-015-0241-3
Efficacy of Methylphenidate Hydrochloride Extended-Release Capsules (Aptensio XR™) in Children and Adolescents with Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder: A Phase III, Randomized, Double-Blind Study
Abstract
Background: Psychostimulants remain first-line treatment options for the management of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). A multilayer extended-release bead methylphenidate capsule (provisional name Aptensio XR™, MPH-MLR) with unique release properties is being investigated for the treatment of ADHD.
Objective: The aim of this study was to assess the efficacy (primary) and safety and tolerability (secondary) of MPH-MLR compared with placebo in children and adolescents aged 6-18 years with ADHD.
Methods: This study was a parallel, double-blind, multicenter, placebo-controlled, forced-dose, phase III study in which patients were randomized to placebo or MPH-MLR 10, 15, 20, or 40 mg given once daily. There were four study phases: (1) 4-week screening/baseline; (2) 1-week, double-blind treatment (DBP); (3) 11-week, open-label, dose-optimization period; and (4) 30-day follow-up call. During the open-label dose-optimization period all patients started with MPH-MLR 10 mg, unless the investigator deemed it necessary to begin at a higher dose, and were titrated to an optimized dose (10, 15, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60 mg; all given once daily) based on response and adverse events (AEs). The primary endpoint was the change from baseline to end of DBP in ADHD Rating Scale, 4th Edition (ADHD-RS-IV) total score. Secondary endpoints included changes in ADHD-RS-IV subscales and Clinical Global Impression-Improvement Scale (CGI-I) at the end of the DBP. The primary analysis was an analysis of covariance including terms for treatment, site, and baseline ADHD-RS-IV total score.
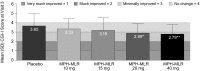
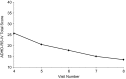
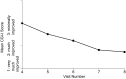
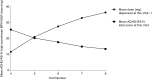
Results: A total of 221 patients completed the DBP. The primary endpoint had a statistically significant difference among treatments (p = 0.0046) and sites (p = 0.0018), and baseline covariate made a significant contribution (p < 0.0001). As the MPH-MLR dose increased, the ADHD-RS-IV total score improved; the 20 and 40 mg doses were statistically different (p = 0.0145 and p = 0.0011, respectively) from placebo. Females responded differently than did males (p = 0.0238); there was a significant difference among treatments for males but not for females, partly because only one-third of subjects were female and partly because some females who received placebo had considerable improvement during the DBP. Similarly, the ADHD-RS-IV subscales and CGI-I scores at the end of the DBP also showed more improvement as the dose of MPH-MLR increased. During the open-label phase, ADHD-RS-IV total scores improved (mean change from baseline -22.5) and correlated as the dose of MPH-MLR increased; CGI-I scores also improved. No unexpected AEs were noted.
Conclusions: Dose-related improvements in ADHD-RS-IV scores that exceeded those of placebo were observed in patients treated with MPH-MLR. No new safety signals were noted.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT01239030.
Figures


References
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). http://www.cdc.gov/nchs/fastats/adhd.htm. Accessed 17 June 2014.
-
- Wolraich M, Brown L, Brown RT, DuPaul G, Earls M, Feldman HM, et al. ADHD: clinical practice guideline for the diagnosis, evaluation, and treatment of attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder in children and adolescents. Pediatrics. 2011;128(5):1007–1022. doi: 10.1542/peds.2011-2654. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Quillivant XR™ (methylphenidate hydrochloride) product information. New York: NextWave Pharmaceuticals (2013). http://www.quillivantxr.com. Accessed 24 July 2013.
-
- Wigal SB, Wigal TL, Kollins SH. Advances in methylphenidate drug delivery systems for ADHD therapy. Adv ADHD. 2006;1:4–7.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

