Three-dimensional Structure of a Kunitz-type Inhibitor in Complex with an Elastase-like Enzyme
- PMID: 25878249
- PMCID: PMC4447985
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M115.647586
Three-dimensional Structure of a Kunitz-type Inhibitor in Complex with an Elastase-like Enzyme
Abstract
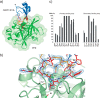
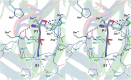
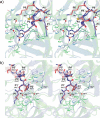
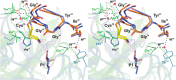
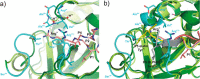
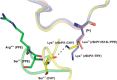
Elastase-like enzymes are involved in important diseases such as acute pancreatitis, chronic inflammatory lung diseases, and cancer. Structural insights into their interaction with specific inhibitors will contribute to the development of novel anti-elastase compounds that resist rapid oxidation and proteolysis. Proteinaceous Kunitz-type inhibitors homologous to the bovine pancreatic trypsin inhibitor (BPTI) provide a suitable scaffold, but the structural aspects of their interaction with elastase-like enzymes have not been elucidated. Here, we increased the selectivity of ShPI-1, a versatile serine protease inhibitor from the sea anemone Stichodactyla helianthus with high biomedical and biotechnological potential, toward elastase-like enzymes by substitution of the P1 residue (Lys(13)) with leucine. The variant (rShPI-1/K13L) exhibits a novel anti-porcine pancreatic elastase (PPE) activity together with a significantly improved inhibition of human neuthrophil elastase and chymotrypsin. The crystal structure of the PPE·rShPI-1/K13L complex determined at 2.0 Å resolution provided the first details of the canonical interaction between a BPTI-Kunitz-type domain and elastase-like enzymes. In addition to the essential impact of the variant P1 residue for complex stability, the interface is improved by increased contributions of the primary and secondary binding loop as compared with similar trypsin and chymotrypsin complexes. A comparison of the interaction network with elastase complexes of canonical inhibitors from the chelonian in family supports a key role of the P3 site in ShPI-1 in directing its selectivity against pancreatic and neutrophil elastases. Our results provide the structural basis for site-specific mutagenesis to further improve the binding affinity and/or direct the selectivity of BPTI-Kunitz-type inhibitors toward elastase-like enzymes.
Keywords: BPTI-Kunitz type; crystal structure; protease inhibitor; protein complex; serine protease; site-directed mutagenesis.
© 2015 by The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, Inc.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Polar Desolvation and Position 226 of Pancreatic and Neutrophil Elastases Are Crucial to their Affinity for the Kunitz-Type Inhibitors ShPI-1 and ShPI-1/K13L.PLoS One. 2015 Sep 15;10(9):e0137787. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0137787. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26372354 Free PMC article.
-
Two variants of the major serine protease inhibitor from the sea anemone Stichodactyla helianthus, expressed in Pichia pastoris.Protein Expr Purif. 2016 Jul;123:42-50. doi: 10.1016/j.pep.2016.03.003. Epub 2016 Mar 16. Protein Expr Purif. 2016. PMID: 26993255
-
Structural insights into serine protease inhibition by a marine invertebrate BPTI Kunitz-type inhibitor.J Struct Biol. 2012 Nov;180(2):271-9. doi: 10.1016/j.jsb.2012.08.009. Epub 2012 Sep 5. J Struct Biol. 2012. PMID: 22975140
-
Structure-function relationship of serine protease-protein inhibitor interaction.Acta Biochim Pol. 2001;48(2):419-28. Acta Biochim Pol. 2001. PMID: 11732612 Review.
-
The bovine basic pancreatic trypsin inhibitor (Kunitz inhibitor): a milestone protein.Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2003 Jun;4(3):231-51. doi: 10.2174/1389203033487180. Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2003. PMID: 12769721 Review.
Cited by
-
Identification and Characterization of Roseltide, a Knottin-type Neutrophil Elastase Inhibitor Derived from Hibiscus sabdariffa.Sci Rep. 2016 Dec 19;6:39401. doi: 10.1038/srep39401. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27991569 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Characterization of Kunitz-Type Protease Inhibitors from Blister Beetles (Coleoptera, Meloidae).Biomolecules. 2022 Jul 15;12(7):988. doi: 10.3390/biom12070988. Biomolecules. 2022. PMID: 35883544 Free PMC article.
-
The Kunitz-Type Protein ShPI-1 Inhibits Serine Proteases and Voltage-Gated Potassium Channels.Toxins (Basel). 2016 Apr 13;8(4):110. doi: 10.3390/toxins8040110. Toxins (Basel). 2016. PMID: 27089366 Free PMC article.
-
The Immunomodulatory Effect of IrSPI, a Tick Salivary Gland Serine Protease Inhibitor Involved in Ixodes ricinus Tick Feeding.Vaccines (Basel). 2019 Oct 12;7(4):148. doi: 10.3390/vaccines7040148. Vaccines (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31614804 Free PMC article.
-
Polar Desolvation and Position 226 of Pancreatic and Neutrophil Elastases Are Crucial to their Affinity for the Kunitz-Type Inhibitors ShPI-1 and ShPI-1/K13L.PLoS One. 2015 Sep 15;10(9):e0137787. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0137787. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26372354 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Debelle L., Tamburro A. M. (1999) Elastin: molecular description and function. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 31, 261–272 - PubMed
-
- Büchler M., Uhl W., Malfertheiner P. (1987) Elastase 1 in Acute Pancreatitis: Research and Clinical Management (Beger H. G., Büchler M. D., eds), pp. 110–117, Springer Berlin Heidelberg, Berlin
-
- Ooyama T., Sakamato H. (1995) Elastase in the prevention of arterial aging and the treatment of atherosclerosis. Ciba Found. Symp. 192, 307–317 - PubMed
-
- Shapiro S. D. (1995) The pathogenesis of emphysema: the elastase:antielastase hypothesis 30 years later. Proc. Assoc. Am. Physicians 107, 346–352 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

