Impact of maternal n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid deficiency on dendritic arbor morphology and connectivity of developing Xenopus laevis central neurons in vivo
- PMID: 25878281
- PMCID: PMC4397605
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4102-14.2015
Impact of maternal n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid deficiency on dendritic arbor morphology and connectivity of developing Xenopus laevis central neurons in vivo
Abstract
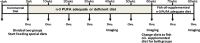
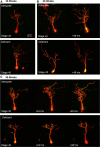
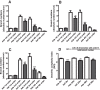
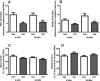
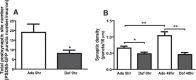
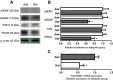
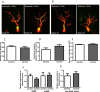
Docosahexaenoic acid (DHA, 22:6n-3) is an essential component of the nervous system, and maternal n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) are an important source for brain development. Here, the impact of DHA on developing central neurons was examined using an accessible in vivo model. Xenopus laevis embryos from adult female frogs fed n-3 PUFA-adequate or deficient diets were analyzed every 10 weeks for up to 60 weeks, when frogs were then switched to a fish oil-supplemented diet. Lipid analysis showed that DHA was significantly reduced both in oocytes and tadpoles 40 weeks after deprivation, and brain DHA was reduced by 57% at 60 weeks. In vivo imaging of single optic tectal neurons coexpressing tdTomato and PSD-95-GFP revealed that neurons were morphologically simpler in tadpoles from frogs fed the deficient diet compared with the adequate diet. Tectal neurons had significantly fewer dendrite branches and shorter dendritic arbor over a 48 h imaging period. Postsynaptic cluster number and density were lower in neurons deprived of n-3 PUFA. Moreover, changes in neuronal morphology correlated with a 40% decrease in the levels of BDNF mRNA and mature protein in the brain, but not in TrkB. Importantly, switching to a fish oil-supplemented diet induced a recovery in DHA content in the frog embryos within 20 weeks and diminished the deprivation effects observed on tectal neurons of Stage 45 tadpoles. Consequently, our results indicate that DHA impacts dendrite maturation and synaptic connectivity in the developing brain, and it may be involved in neurotrophic support by BDNF.
Keywords: DHA; Xenopus laevis; dendrite; in vivo imaging; maternal diet; tectal neuron.
Copyright © 2015 the authors 0270-6474/15/356079-14$15.00/0.
Figures

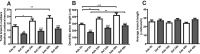
Similar articles
-
BDNF increases synapse density in dendrites of developing tectal neurons in vivo.Development. 2006 Jul;133(13):2477-86. doi: 10.1242/dev.02409. Epub 2006 May 25. Development. 2006. PMID: 16728478
-
DSCAM differentially modulates pre- and postsynaptic structural and functional central connectivity during visual system wiring.Neural Dev. 2018 Sep 15;13(1):22. doi: 10.1186/s13064-018-0118-5. Neural Dev. 2018. PMID: 30219101 Free PMC article.
-
Cell-autonomous TrkB signaling in presynaptic retinal ganglion cells mediates axon arbor growth and synapse maturation during the establishment of retinotectal synaptic connectivity.J Neurosci. 2007 Mar 7;27(10):2444-56. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4434-06.2007. J Neurosci. 2007. PMID: 17344382 Free PMC article.
-
Docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) and the developing central nervous system (CNS) - Implications for dietary recommendations.Biochimie. 2011 Jan;93(1):7-12. doi: 10.1016/j.biochi.2010.05.005. Epub 2010 May 15. Biochimie. 2011. PMID: 20478353 Review.
-
Mechanisms of n-3 fatty acid-mediated development and maintenance of learning memory performance.J Nutr Biochem. 2010 May;21(5):364-73. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2009.11.003. Epub 2010 Mar 16. J Nutr Biochem. 2010. PMID: 20233652 Review.
Cited by
-
Epigenetic regulation of GABAergic differentiation in the developing brain.Front Cell Neurosci. 2022 Sep 23;16:988732. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2022.988732. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 36212693 Free PMC article.
-
A predictive model of offspring congenital heart disease based on maternal risk factors during pregnancy: a hospital based case-control study in Nanchong City.Int J Med Sci. 2020 Oct 22;17(18):3091-3097. doi: 10.7150/ijms.48046. eCollection 2020. Int J Med Sci. 2020. PMID: 33173430 Free PMC article.
-
Reversible developmental stasis in response to nutrient availability in the Xenopus laevis central nervous system.J Exp Biol. 2017 Feb 1;220(Pt 3):358-368. doi: 10.1242/jeb.151043. Epub 2016 Nov 10. J Exp Biol. 2017. PMID: 27875263 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of Effective and Practical Euthanasia Methods for Larval African Clawed Frogs (Xenopus laevis).J Am Assoc Lab Anim Sci. 2020 May 1;59(3):269-274. doi: 10.30802/AALAS-JAALAS-19-000141. Epub 2020 Mar 12. J Am Assoc Lab Anim Sci. 2020. PMID: 32164797 Free PMC article.
-
Docosahexaenoic Acid Rescues Synaptogenesis Impairment and Long-Term Memory Deficits Caused by Postnatal Multiple Sevoflurane Exposures.Biomed Res Int. 2016;2016:4062579. doi: 10.1155/2016/4062579. Epub 2016 Aug 11. Biomed Res Int. 2016. PMID: 27597963 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
