Predictive value of elevated neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio for left ventricular systolic dysfunction in patients with non ST-elevated acute coronary syndrome
- PMID: 25878635
- PMCID: PMC4386178
- DOI: 10.12669/pjms.311.5967
Predictive value of elevated neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio for left ventricular systolic dysfunction in patients with non ST-elevated acute coronary syndrome
Abstract
Objective: We aimed to study the predictive value of the neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) for left ventricular systolic dysfunction (LVSD) in patients with non ST-elevated acute coronary syndrome (NST-ACS).
Methods: A total of 405 patients (mean age 62 years and 75% male) with NST-ACS were included in the study. The study population was divided into tertiles based on admission NLR values. The low, medium and high tertiles defined as NLR≤1.81 (n=135), 1.81<NLR≤3.2 (n=135) and NLR>3.2 (n=135), respectively.
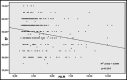
Results: The patients in the high NLR group were older (p<0.001), have higher rate of diabetes mellitus (p=0.028) and non-ST elevated myocardial infarction (NSTEMI) (p<0.001) and have lower left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) (p<0.001). Baseline WBC (p=0.02) and neutrophil (p<0.001) levels and NLR (p<0.001) were significantly higher, baseline hemoglobin (p=0.044), hematocrit (p=0.019) and lymphocyte (p<0.001) levels were significantly lower in the high NLR group. NLR was negatively correlated with LVEF in correlation analysis. An NLR >3.2 and age ≥70 were found to be an independent predictor of systolic dysfunction in multivariate analyses.
Conclusion: An NLR >3.2 is a useful predictor for LVSD in patients with NST-ACS. The practice of using an NLR count on admission may be useful for identifying high-risk patients and their associated treatment methods.
Keywords: Acute coronary syndrome; Ejection fraction; Myocardial infarction; Neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio; Systolic dysfunction.
Figures
References
-
- Libby P, Ridker PM, Maseri A. Inflammation and atherosclerosis. Circulation. 2002;105(9):1135–1143. - PubMed
-
- Lee C, Folsom AR, Nieto FJ, Chambless LE, Shahar E, Wolfe DA. White blood cell count and incidence of coronary heart disease and ischemic stroke and mortality from cardiovascular disease in African-American and White men and women: atherosclerosis risk in communities study. Am J Epidemiol. 2001;154(8):758–764. - PubMed
-
- Haim M, Boyko V, Goldbourt U, Battler A, Behar S. Predictive value of elevated white blood cell count in patients with preexisting coronary heart disease: the Bezafibrate Infarction Prevention Study. Arch Intern Med. 2004;164(4):433–439. - PubMed
-
- Horne BD, Anderson JL, John JM, Weaver A, Bair TL, Jensen KR, et al. Which white blood cell subtypes predict increased cardiovascular risk? J Am Coll Cardiol. 2005;45(10):1638–1643. - PubMed
-
- Cooper HA, Exner DV, Waclawiw MA, Domanski MJ. White blood cell count and mortality in patients with ischemic and non-ischemic left ventricular systolic dysfunction (an analysis of the Studies of Left Ventricular Dysfunction [SOLVD] Am J Cardiol. 1999;84(3):252–257. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources