DIEP Flap Breast Reconstruction Using 3-dimensional Surface Imaging and a Printed Mold
- PMID: 25878927
- PMCID: PMC4387138
- DOI: 10.1097/GOX.0000000000000288
DIEP Flap Breast Reconstruction Using 3-dimensional Surface Imaging and a Printed Mold
Abstract
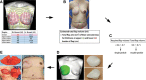
Recent advances in 3-dimensional (3D) surface imaging technologies allow for digital quantification of complex breast tissue. We performed 11 unilateral breast reconstructions with deep inferior epigastric artery perforator (DIEP) flaps (5 immediate, 6 delayed) using 3D surface imaging for easier surgery planning and 3D-printed molds for shaping the breast neoparenchyma. A single- or double-pedicle flap was preoperatively planned according to the estimated tissue volume required and estimated total flap volume. The DIEP flap was then intraoperatively shaped with a 3D-printed mold that was based on a horizontally inverted shape of the contralateral breast. Cosmetic outcomes were assessed as satisfactory, as confirmed by the postoperative 3D measurements of bilateral breasts. We believe that DIEP flap reconstruction assisted with 3D surface imaging and a 3D-printed mold is a simple and quick method for rebuilding a symmetric breast.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Koshima I, Soeda S. Inferior epigastric artery skin flaps without rectus abdominis muscle. Br J Plast Surg. 1989;42:645–648. - PubMed
-
- Nahabedian MY, Momen B, Galdino G, et al. Breast reconstruction with the free TRAM or DIEP flap: patient selection, choice of flap, and outcome. Plast Reconstr Surg. 2002;110:466–475; discussion 476–477. - PubMed
-
- Kovacs L, Eder M, Hollweck R, et al. New aspects of breast volume measurement using 3-dimensional surface imaging. Ann Plast Surg. 2006;57:602–610. - PubMed
-
- Kovacs L, Eder M, Hollweck R, et al. Comparison between breast volume measurement using 3D surface imaging and classical techniques. Breast. 2007;16:137–145. - PubMed
-
- Sotsuka Y, Nishimoto S. Making three-dimensional mandible models using a personal three-dimensional printer. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2014;67:576–578. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
